3D Printed Silicones with Shape Memory
- PMID: 28680078
- PMCID: PMC5498669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04663-z
3D Printed Silicones with Shape Memory
Abstract
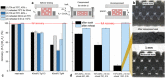
Direct ink writing enables the layer-by-layer manufacture of ordered, porous structures whose mechanical behavior is driven by architecture and material properties. Here, we incorporate two different gas filled microsphere pore formers to evaluate the effect of shell stiffness and Tg on compressive behavior and compression set in siloxane matrix printed structures. The lower Tg microsphere structures exhibit substantial compression set when heated near and above Tg, with full structural recovery upon reheating without constraint. By contrast, the higher Tg microsphere structures exhibit reduced compression set with no recovery upon reheating. Aside from their role in tuning the mechanical behavior of direct ink write structures, polymer microspheres are good candidates for shape memory elastomers requiring structural complexity, with potential applications toward tandem shape memory polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shimazaki Y, Nozo S, Inoue T. Shock-absorption properties of functionally graded EVA laminates for footwear design. Polymer Testing. 2016;54:98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2016.04.024. - DOI
-
- Zhang ZH, Provis JL, Reid A, Wang H. Mechanical, thermal insulation, thermal resistance and acoustic absorption properties of geopolymer foam concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015;62:97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2015.03.013. - DOI
-
- Mrozek RA, Gold CS, Leighliter B, Sietins JM, Lenhart JL. Open pore, elastomeric scaffolds through frustrated particle collapse. J. Mater. Sci. 2016;51:10761–10774. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0288-7. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

