Evaluation of Renal Function in Alzheimer's Disease and Geriatric Patients: Results from a Turkish Two-center Study
- PMID: 28680350
- PMCID: PMC5471660
- DOI: 10.1515/jomb-2016-0028
Evaluation of Renal Function in Alzheimer's Disease and Geriatric Patients: Results from a Turkish Two-center Study
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a severe multifactorial neurodegenerative proteopathy associated with advanced age. Discrepancies in the renal function of these patients compared to geriatric patients with dementia have rarely been reported. In this study, we aimed to disclose the importance of associated renal changes for the pathogenesis of AD.
Methods: Patients with AD (n=107) and geriatric patients with dementia and without dementia (n=124) (231 patients in total) from Dokuz Eylul and Cukurova University Hospitals were enrolled in the study. We measured serum Na, K, Cl, Ca, BUN, creatinine, total protein levels and MDRD [eGFR] in all groups.
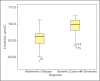
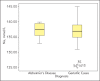
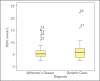
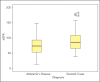
Results: From Izmir Center, the first study arm consisted of patients with AD dementia (n=74), and the second arm included geriatric patients with dementia (n=79). From Adana, 78 patients were recruited to the study, of which 33 were with AD and 45 were geriatric patients without dementia. When we analyzed comparatively the AD and geriatric dementia patients study arms, a statistically significant difference was observed both in the median age (p<0.001), as well as in the biochemical parameters from Izmir Center: Na (p<0.001), K (p<0.001), Cl (p<0.05), Ca (p<0.001), BUN (p<0.05), creatinine (p<0.001), total protein (p<0.001) and MDRD [eGFR] (p<0.001). However, these were not significantly different between AD and geriatric patients without dementia in the Adana group.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that renal function is prone to alterations in different age groups of patients with AD. However, there is no conclusive evidence that renal function is one of the risk factors in AD.
Uvod: Alchajmerova bolest (AB) predstavlja tešku multifaktorijalnu neurodegenerativnu proteopatiju koja je povezana sa starenjem. Dosad nije bilo mnogo izveštaja o razlikama u bubrežnoj funkciji kod obolelih od AB i kod gerijatrijskih pacijenata sa demencijom. U ovoj studiji, cilj je bio da se otkrije važnost povezanih promena bubrežne funkcije u patogenezi AB.
Metode: Studija je obuhvatila obolele od AB (n=107) i gerijatrijske pacijente sa demencijom i bez demencije (n=124) (ukupno 231 pacijent) iz bolnica Dokuz Eylul i Univerziteta Cukurova. U svim grupama, izmerili smo serumske nivoe Na, K, Cl, Ca, BUN, kreatinina, ukupnog proteina i MDRD (eGFR).
Rezultati: Iz centra Izmir, kao jednog od dva centra u kojima je studija sprovedena, uključeni su pacijenti sa demencijom AB (n=74) i gerijatrijski pacijenti sa demencijom (n=79). Iz centra Adana, u studiju je uključeno 78 pacijenata, od kojih je 33 imalo AB, dok su 45 bili gerijatrijski pacijenti bez demencije. Kada smo uporedo analizirali pacijente sa AD i gerijatrijskom demencijom, uočene su statistički značajne razlike kako u prosečnoj dobi (p<0,001) tako i u biohemijskim parametrima iz centra Izmir: Na (p<0,001), K (p<0,001), Cl (p<0,001), Ca (p<0,001), BUN (p<0,05), kreatinin (p<0,001), ukupni protein (p<0,001) i MDRD (eGFR) (p<0,001). Međutim, ovi parametri se u grupi Adana nisu značajno razlikovali između obolelih od AB i gerijatrijskih pacijenata bez demencije.
Zaključak: Naši rezultati ukazuju na to da je bubrežna funkcija podložna alteracijama u različitim starosnim grupama obolelih od AB. Međutim, nema čvrstih dokaza da je bubrežna funkcija jedan od faktora rizika za AB.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; dementia; renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement The authors stated that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Effects of donepezil on liver and kidney functions for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.J Integr Neurosci. 2017;16(3):335-346. doi: 10.3233/JIN-170020. J Integr Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28891516
-
A Turkish 3-center study evaluation of serum folic acid and vitamin B12 levels in Alzheimer disease.Turk J Med Sci. 2015;45(5):1159-66. doi: 10.3906/sag-1406-136. Turk J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26738362
-
The importance of brain banking for dementia practice: the first experience of Turkey.Cell Tissue Bank. 2020 Sep;21(3):367-375. doi: 10.1007/s10561-020-09835-2. Epub 2020 May 20. Cell Tissue Bank. 2020. PMID: 32435952
-
NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2018 Apr;14(4):535-562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. Alzheimers Dement. 2018. PMID: 29653606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the development of biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease: from CSF total tau and Abeta(1-42) proteins to phosphorylated tau protein.Brain Res Bull. 2003 Aug 15;61(3):243-53. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(03)00087-x. Brain Res Bull. 2003. PMID: 12909294 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of creatinine level with neurodegenerative disorders: a prospective cohort study and Mendelian randomization analysis.Neurol Sci. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s10072-025-08361-x. Online ahead of print. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40643880
-
iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Analysis of APP Transgenic Mouse Urine Exosomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):672. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010672. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614115 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of Renal Drug Transporters in a Mouse Model of Familial Alzheimer's Disease.J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jul;108(7):2484-2489. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 30825461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ulusu NN, Yilmaz G, Erbayraktar Z, Evlice AT, Aras S, Yener G, Avci A. A Turkish three-center study evaluation of serum folic acid and vitamin B12 levels in Alzheimer’s Disease. Turk J Med Sci. 2015;45(5):59–66. - PubMed
-
- Hampel H, Lista S, Teipel SJ, Garaci F, Nisticò R, Blennow K. et al. Perspective on future role of biological markers in clinical therapy trials of Alzheimer’s disease: a long-range point of view beyond 2020. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;88(4):26–49. - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M, Riellae M. Chronic kidney disease and the aging population. Arab J Nephrol Transplant. 2014;7(1):7–11. - PubMed
-
- Galan A, Carletti BE, Morgaz J, Granados MM, Mesa I, Navarrete R. et al. Comparative study of select biochemical markers in cerebrospinal fluid of healthy dogs before and after treatment with nutraceuticals. Vet Clin Pathol. 2014;43(1):2–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
