Validation of different pediatric triage systems in the emergency department
- PMID: 28680520
- PMCID: PMC5496831
- DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2017.03.010
Validation of different pediatric triage systems in the emergency department
Abstract
Background: Triage system in children seems to be more challenging compared to adults because of their different response to physiological and psychosocial stressors. This study aimed to determine the best triage system in the pediatric emergency department.
Methods: This was a prospective observational study. This study was divided into two phases. The first phase determined the inter-rater reliability of five triage systems: Manchester Triage System (MTS), Emergency Severity Index (ESI) version 4, Pediatric Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale (CTAS), Australasian Triage Scale (ATS), and Ramathibodi Triage System (RTS) by triage nurses and pediatric residents. In the second phase, to analyze the validity of each triage system, patients were categorized as two groups, i.e., high acuity patients (triage level 1, 2) and low acuity patients (triage level 3, 4, and 5). Then we compared the triage acuity with actual admission.
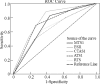
Results: In phase I, RTS illustrated almost perfect inter-rater reliability with kappa of 1.0 (P<0.01). ESI and CTAS illustrated good inter-rater reliability with kappa of 0.8-0.9 (P<0.01). Meanwhile, ATS and MTS illustrated moderate to good inter-rater reliability with kappa of 0.5-0.7 (P<0.01). In phase II, we included 1 041 participants with average age of 4.7±4.2 years, of which 55% were male and 45% were female. In addition 32% of the participants had underlying diseases, and 123 (11.8%) patients were admitted. We found that ESI illustrated the most appropriate predicting ability for admission with sensitivity of 52%, specificity of 81%, and AUC 0.78 (95%CI 0.74-0.81).
Conclusion: RTS illustrated almost perfect inter-rater reliability. Meanwhile, ESI and CTAS illustrated good inter-rater reliability. Finally, ESI illustrated the appropriate validity for triage system.
Keywords: Emergency department; Pediatric; Triage.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to the publication of this paper.
References
-
- Morris ZS, Boyle A, Beniuk K, Robinson S. Emergency department crowding:towards an agenda for evidence-based intervention. Emerg Med J. 2012;29(6):460–6. - PubMed
-
- Cain P, Waldrop RD, Jones J. Improved pediatric patient flow in a general emergency department by altering triage criteria. Acad Emerg Med. 1996;3(1):65–71. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes CMB, Tanabe P, Gilboy N, Johnson LA, McNair RS, Rosenau AM, et al. Five-level triage:a report from the ACEP/ENA five-level triage task force. J Emerg Nurs. 2005;31(1):39–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources