Atrial flutter in a patient with atrial septal defect and anomalous venous drainage: unusual approach for ablation
- PMID: 28680604
- PMCID: PMC5494410
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.998
Atrial flutter in a patient with atrial septal defect and anomalous venous drainage: unusual approach for ablation
Abstract
Atrial flutter ablation in CHD (Congenital Heart Disease) patients is a challenging procedure because of the possibility of multiple circuits. Electroanatomical mapping and pacing maneuvers are crucial to determine critical isthmus. Moreover, vascular abnormalities and residual cardiac defects need to be known before the ablation to decide the better strategy for ablation.
Keywords: Ablation; atrial flutter; congenital heart disease; vascular abnormalities.
Figures


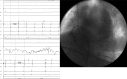
References
-
- Chan, D. , Van Hare G., Mackall J., Carlson M., and Waldo A.. 2000. Importance of atrial flutter ishtmus in postoperative intra‐atrial reentrant tachycardia. Circulation 102:1283–1289. - PubMed
-
- Triedman, J. K. , Alexander M., Berul C., Bevilacqua L., and Walsh E.. 2001. Electroanatomical mapping of entrained and exit zones in patients with repaired congenital heart disease and intra‐atrial reentrant tachycardia. Circulation 103:2060–2065. - PubMed
-
- El Yamman, M. , Asirvatham S., Kapa S., Barrett R., Packer D., and Porter C. B.. 2009. Methods to access the surgically excluded cavotricuspid isthmus for complete ablation of typical atrial flutter in patients with congenital heart defects. Heart Rhythm 6:949–956. - PubMed
-
- Guenther, K. , Marrouche M., and Ruef J.. 2007. Ablation of atrial flutter by the femoral approach in the absence of inferior vena cava. Europace 2007; 9: 1073–1074. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

