Ziehl-Neelsen sputum smear microscopy image database: a resource to facilitate automated bacilli detection for tuberculosis diagnosis
- PMID: 28680911
- PMCID: PMC5492794
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.2.027503
Ziehl-Neelsen sputum smear microscopy image database: a resource to facilitate automated bacilli detection for tuberculosis diagnosis
Abstract
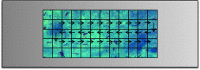
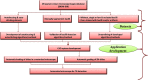
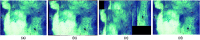
Ziehl-Neelsen stained microscopy is a crucial bacteriological test for tuberculosis detection, but its sensitivity is poor. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) recommendation, 300 viewfields should be analyzed to augment sensitivity, but only a few viewfields are examined due to patient load. Therefore, tuberculosis diagnosis through automated capture of the focused image (autofocusing), stitching of viewfields to form mosaics (autostitching), and automatic bacilli segmentation (grading) can significantly improve the sensitivity. However, the lack of unified datasets impedes the development of robust algorithms in these three domains. Therefore, the Ziehl-Neelsen sputum smear microscopy image database (ZNSM iDB) has been developed, and is freely available. This database contains seven categories of diverse datasets acquired from three different bright-field microscopes. Datasets related to autofocusing, autostitching, and manually segmenting bacilli can be used for developing algorithms, whereas the other four datasets are provided to streamline the sensitivity and specificity. All three categories of datasets were validated using different automated algorithms. As images available in this database have distinctive presentations with high noise and artifacts, this referral resource can also be used for the validation of robust detection algorithms. The ZNSM-iDB also assists for the development of methods in automated microscopy.
Keywords: autofocusing; automated microscopy; autostitching; bacilli segmentation; computer-aided diagnosis; conventional microscopy image database; tuberculosis.
Figures



References
-
- WHO, TB Global Report (2015).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

