Aspergillus colonization in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 28680996
- PMCID: PMC5490329
- DOI: 10.18869/acadpub.cmm.1.3.45
Aspergillus colonization in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) has been recognized as a risk factor for invasive aspergillosis. Airway colonization by Aspergillus species is a common feature of chronic pulmonary diseases. Nowadays, the incidence of COPD has increased in critically ill patients. The aim of the present study was to isolate and identify Aspergillus colonies in the respiratory tract of COPD patients.
Materials and methods: This study was performed on 50 COPD patients, who were aged above 18 years, and were in intensive care units of three hospitals in Sari, Iran, for at least six days. All the samples obtained from sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage, and tracheal aspirates were cultured for fungi each week. According to the conventional techniques, Aspergillus isolates were initially based on growth and standard morphological characteristics. To confirm the identification of grown Aspergillus, the partial beta-tubulin gene was sequenced using specific primers.
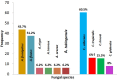
Results: A total of 50 patients, who met our inclusion criteria, were enrolled in the study during 2012-14. The results showed that 27 (54%) and 23 (46%) of the participants were male and female, respectively. The majority of the patients developed dyspnea followed by hemoptysis, chest pain, and high fever. Corticosteroids and broad-spectrum antibacterial agents were administered to 75% and 80% of the patients, respectively. Based on the conventional and molecular approaches, A. fumigatus (seven cases; 43.7%), A. flavus (five cases; 31.2%), A. niger (one case; 6.2%), A. terreus (one case; 6.2%), A. orezea (one case; 6.2%), and A. tubingensis (one case; 6.2%) were recovered.
Conclusion: Recovery of Aspergillus species from the respiratory tract of COPD patients with pneumonia indicates two possibilities: either colonization or invasive aspergillosis.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Sequence Analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agusti AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187(4):347–65. - PubMed
-
- Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, Barnes PJ, Buist SA, Calverley P, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176(6):532–55. - PubMed
-
- Chung KF, Adcock IM. Multifaceted mechanisms in COPD: inflammation, immunity, and tissue repair and destruction. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(6):1334–56. - PubMed
-
- Yu VL, Muder RR, Poorsattar A. Significance of isolation of Aspergillus from the respiratory tract in diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis Results from a three-year prospective study. Am J Med. 1986;81(2):249–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous