Hydrocarbon degradation potential and plant growth-promoting activity of culturable endophytic bacteria of Lotus corniculatus and Oenothera biennis from a long-term polluted site
- PMID: 28681302
- PMCID: PMC5570797
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-017-9496-1
Hydrocarbon degradation potential and plant growth-promoting activity of culturable endophytic bacteria of Lotus corniculatus and Oenothera biennis from a long-term polluted site
Abstract
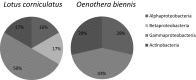
Many endophytic bacteria exert beneficial effects on their host, but still little is known about the bacteria associated with plants growing in areas heavily polluted by hydrocarbons. The aim of the study was characterization of culturable hydrocarbon-degrading endophytic bacteria associated with Lotus corniculatus L. and Oenothera biennis L. collected in long-term petroleum hydrocarbon-polluted site using culture-dependent and molecular approaches. A total of 26 hydrocarbon-degrading endophytes from these plants were isolated. Phylogenetic analyses classified the isolates into the phyla Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria. The majority of strains belonged to the genera Rhizobium, Pseudomonas, Stenotrophomonas, and Rhodococcus. More than 90% of the isolates could grow on medium with diesel oil, approximately 20% could use n-hexadecane as a sole carbon and energy source. PCR analysis revealed that 40% of the isolates possessed the P450 gene encoding for cytochrome P450-type alkane hydroxylase (CYP153). In in vitro tests, all endophytic strains demonstrated a wide range of plant growth-promoting traits such as production of indole-3-acetic acid, hydrogen cyanide, siderophores, and phosphate solubilization. More than 40% of the bacteria carried the gene encoding for the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase (acdS). Our study shows that the diversity of endophytic bacterial communities in tested plants was different. The results revealed also that the investigated plants were colonized by endophytic bacteria possessing plant growth-promoting features and a clear potential to degrade hydrocarbons. The properties of isolated endophytes indicate that they have the high potential to improve phytoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-polluted soils.
Keywords: Endophytic bacteria; Lotus corniculatus L.; Oenothera biennis L.; Petroleum hydrocarbons; Plant growth-promoting mechanisms; Plant-bacteria interactions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diversity of endophytic bacteria in Lolium perenne and their potential to degrade petroleum hydrocarbons and promote plant growth.Chemosphere. 2014 Dec;117:40-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.055. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Chemosphere. 2014. PMID: 24954306
-
Petroleum degradation by endophytic Streptomyces spp. isolated from plants grown in contaminated soil of southern Algeria.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018 Jan;147:602-609. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2018. PMID: 28923725
-
Endophytic Bacteria Associated with Hieracium piloselloides: Their Potential for Hydrocarbon-Utilizing and Plant Growth-Promotion.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2015;78(13-14):860-70. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2015.1051200. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2015. PMID: 26167752
-
Beneficial role of bacterial endophytes in heavy metal phytoremediation.J Environ Manage. 2016 Jun 1;174:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.02.047. Epub 2016 Mar 15. J Environ Manage. 2016. PMID: 26989941 Review.
-
Endophytic bacteria: prospects and applications for the phytoremediation of organic pollutants.Chemosphere. 2014 Dec;117:232-42. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.078. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Chemosphere. 2014. PMID: 25078615 Review.
Cited by
-
Endophytic Bacillus velezensis strain B-36 is a potential biocontrol agent against lotus rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Apr;128(4):1153-1162. doi: 10.1111/jam.14542. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31808212 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Phytoremediation Potential: A Comprehensive Study of Flora Inventory and Soil Heavy Metal Contents in the Northeastern Mining Districts of Morocco.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 30;13(13):1811. doi: 10.3390/plants13131811. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999651 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds Produced by Endophytic Bacteria and Their Plant Hosts-An Insight into the World of Chosen Herbaceous Ruderal Plants in Central Europe.Molecules. 2024 Sep 19;29(18):4456. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184456. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diesel degrading bacterial endophytes with plant growth promoting potential isolated from a petroleum storage facility.3 Biotech. 2019 Jan;9(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1561-z. Epub 2019 Jan 5. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 30622873 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing microbial allies: enhancing black alder resilience to PAH stress through microbial symbiosis.Front Plant Sci. 2025 May 8;16:1552258. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1552258. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40406720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbamondi GR, Tommonaro G, Weyens N, Thijs S, Sillen W, Gkorezis P, Iodice C, Rangel WM, Nicolaus B, Vangronsveld J. Plant growth-promoting effects of rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria associated with different tomato cultivars and new tomato hybrids. Chem Biol Technol Agric. 2016;3:1. doi: 10.1186/s40538-015-0051-3. - DOI
-
- Andersen JB, Koch B, Nielsen TH, Sørensen D, Hansen M, Nybroe O, Christophersen C, Sørensen J, Molin S, Givskov M. Surface motility in Pseudomonas sp. DSS73 is required for efficient biological containment of the root-pathogenic microfungi Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium ultimum. Microbiology. 2003;149:37–46. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.25859-0. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

