Interleukin-9 over-expression and T helper 9 polarization in systemic sclerosis patients
- PMID: 28681919
- PMCID: PMC5629425
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13009
Interleukin-9 over-expression and T helper 9 polarization in systemic sclerosis patients
Abstract
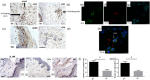
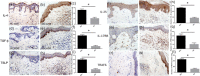
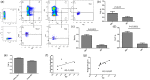
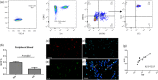
T helper 9 (Th9) cells and interleukin (IL)-9 are involved in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases. The exact role of IL-9 and Th9 cells in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) have not yet been studied adequately. IL-9, IL-9R, transcription factor PU.1 (PU.1), IL-4, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β expression were assessed in skin and kidney biopsies of SSc patients and healthy controls (HC) by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The cellular source of IL-9 was also analysed by confocal microscopy analysis. Peripheral IL-9-producing cells were also studied by flow cytometry. The functional relevance of IL-9 increased expression in SSc was also investigated. Our results demonstrated a strong expression of IL-9, IL-9R, IL-4, TSLP and TGF-β in skin tissues of patients with both limited and diffuse SSc. IL-9 expression was observed mainly in the context of skin infiltrating mononuclear cells and keratinizing squamous epithelium. IL-9 over-expression was also observed in renal biopsies of patients with SSc. IL-9 producing cells in the skin were identified as Th9 cells. Similarly, Th9 cells were expanded and were the major source of IL-9 among SSc peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), their percentage being correlated directly with the modified Rodnan skin score. Infiltrating mononuclear cells, mast cells and neutrophils expressed IL-9R. In in-vitro studies stimulation with rIL-9 significantly induced NET (neutrophil extracellular traps) release by dying cells (NETosis) in neutrophils, expansion of mast cells and increase of anti-systemic scleroderma 70 (Scl70) production by B cells. Our findings suggest that Th9 cells and IL-9 could be implicated in the pathogenesis of SSc.
Keywords: IL-9; ILC2; Th9; systemic sclerosis.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential involvement of IL-9 and Th9 cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Dec;54(12):2264-72. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev252. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26178600
-
Th 9 cells in Behçet disease: Possible involvement of IL-9 in pulmonary manifestations.Immunol Lett. 2019 Jul;211:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 7. Immunol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31075294
-
Effect of crosstalk between Th17 and Th9 cells on the activation of dermal vascular smooth muscle cells in systemic scleroderma and regulation of tanshinone IIA.An Bras Dermatol. 2022 Nov-Dec;97(6):716-728. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2021.11.008. Epub 2022 Sep 15. An Bras Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36117047 Free PMC article.
-
Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):55-68. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0601-1. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27858144 Review.
-
T Helper 9 Cells: A New Player in Immune-Related Diseases.DNA Cell Biol. 2019 Oct;38(10):1040-1047. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.4729. Epub 2019 Aug 16. DNA Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31414895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-9 blockade attenuates inflammation in a murine model of mechanical ventilation-induced lung injury by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Aug;30(4):1395-1406. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-00947-7. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35296962
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs Play a Role in the Pathogenesis of Psoriatic Arthritis by Regulating MicroRNAs and Genes Involved in Inflammation and Metabolic Syndrome.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 16;9:1533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01533. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30061880 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney involvement in systemic sclerosis: From pathogenesis to treatment.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2018 Feb;3(1):43-52. doi: 10.1177/2397198318758607. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2018. PMID: 35382123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting the role of T cells in the pathogenesis of Sjögren's syndrome for therapeutic treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 28;13:995895. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.995895. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-19b exacerbates systemic sclerosis through promoting Th9 cells.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114565. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114565. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39083380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brembilla NC, Chizzolini C. T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis with a focus on Th17 cells. Eur Cytokine Netw 2012; 23:128–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

