Validation of the mSOAR and SOAR scores to predict early mortality in Chinese acute stroke patients
- PMID: 28683108
- PMCID: PMC5500336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180444
Validation of the mSOAR and SOAR scores to predict early mortality in Chinese acute stroke patients
Abstract
Background: It is unclear in Chinese patients with acute stroke how the SOAR (stroke subtype, Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project classification, age, and prestrike modified Rankin) and mSOAR (modified-SOAR) scores performed in predicting discharge mortality and 3-month mortality. We aimed to validate the predictability of these scores in this cohort.
Methods: Data from the China National Stroke Registry (CNSR) study was used to perform the mSOAR and SOAR scores for predicting the discharge and 3-month mortality in acute stroke patients.
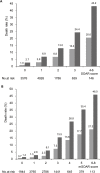
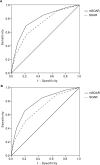
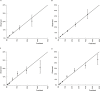
Results: A total of 11073 acute stroke patients were included in present study. The increased mSOAR and SOAR scores were closely related to higher death risk in acute stroke patients. For discharge mortality, the area under the receiver-operator curve (AUC) of the mSOAR and SOAR scores were 0.784 (95% CI 0.761-0.807) and 0.722 (95% CI: 0.698-0.746). For 3-month mortality, they were 0.787 (95% CI: 0.771-0.803) and 0.704 (95% CI: 0.687-0.721), respectively. The mSOAR and SOAR scores showed significant correlation between the predicted and observed probabilities of discharge mortality (mSOAR: r = 0.945, P = 0.001; SOAR: r = 0.994, P<0.001) and 3-month mortality (mSOAR: r = 0.984, P<0.001; SOAR: r = 0.999; P<0.001).
Conclusions: The mSOAR score predicted reliably the risk of death in Chinese acute stroke patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Krishnamurthi RV, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, et al. Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet Global health. 2013;1(5):e259–81. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70089-5 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4181351. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim BJ, Han MK, Park TH, Park SS, Lee KB, Lee BC, et al. Low-Versus Standard-Dose Alteplase for Ischemic Strokes Within 4.5 Hours: A Comparative Effectiveness and Safety Study. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2015;46(9):2541–8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010180 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Machado C, Pinho J, Alves JN, Santos AF, Ferreira Mdo C, Abreu MJ, et al. Five-Year Outcome in Stroke Patients Submitted to Thrombolysis. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2015;46(8):2312–4. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009842 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gensicke H, Strbian D, Zinkstok SM, Scheitz JF, Bill O, Hametner C, et al. Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients Dependent on the Daily Help of Others Before Stroke. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2016;47(2):450–6. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011674 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

