Is Type 2 Diabetes a Glycogen Storage Disease of Pancreatic β Cells?
- PMID: 28683284
- PMCID: PMC5890904
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.05.014
Is Type 2 Diabetes a Glycogen Storage Disease of Pancreatic β Cells?
Abstract
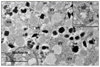
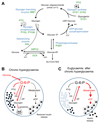
Elevated plasma glucose leads to pancreatic β cell dysfunction and death in type 2 diabetes. Glycogen accumulation, due to impaired metabolism, contributes to this "glucotoxicity" via dysregulated biochemical pathways promoting β cell dysfunction. Here, we review emerging data, and re-examine published findings, on the role of glycogen in β cells in normoglycemia and in diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes; glycogen; insulin; pancreatic β cell.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Andersson LE, Nicholas LM, Filipsson K, Sun J, Medina A, Al-Majdoub M, Fex M, Mulder H, Spegel P. Glycogen metabolism in the glucose-sensing and supply-driven β-cell. FEBS Lett. 2016;590:4242–4251. - PubMed
-
- Anello M, Lupi R, Spampinato D, Piro S, Masini M, Boggi U, Del Prato S, Rabuazzo AM, Purrello F, Marchetti P. Functional and morphological alterations of mitochondria in pancreatic beta cells from type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2005;48:282–289. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft FM. The Walter B. Cannon Physiology in Perspective Lecture, 2007. ATP-sensitive K+ channels and disease: from molecule to malady. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;293:E880–889. - PubMed
-
- Ashcroft SJH, Randle PJ. Glucose 6-phosphatase activity of mouse pancreatic islets. Nature. 1968;5156:857–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

