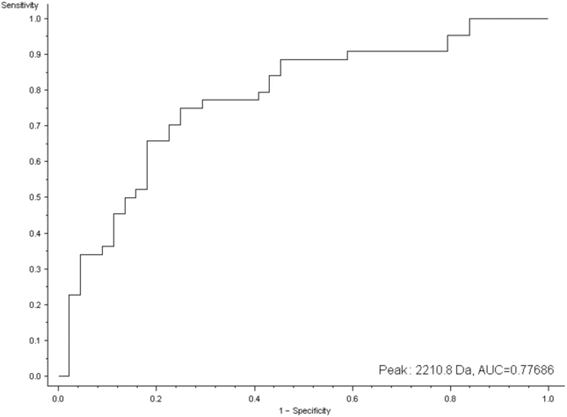
MALDI-TOF-MS analysis in discovery and identification of serum proteomic patterns of ovarian cancer
- PMID: 28683725
- PMCID: PMC5501370
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3467-2
MALDI-TOF-MS analysis in discovery and identification of serum proteomic patterns of ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Due to high mortality and lack of efficient screening, new tools for ovarian cancer (OC) diagnosis are urgently needed. To broaden the knowledge on the pathological processes that occur during ovarian cancer tumorigenesis, protein-peptide profiling was proposed.
Methods: Serum proteomic patterns in samples from OC patients were obtained using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF). Eighty nine serum samples (44 ovarian cancer and 45 healthy controls) were pretreated using solid-phase extraction method. Next, a classification model with the most discriminative factors was identified using chemometric algorithms. Finally, the results were verified by external validation on an independent test set of samples.
Results: Main outcome of this study was an identification of potential OC biomarkers by applying liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Application of this novel strategy enabled the identification of four potential OC serum biomarkers (complement C3, kininogen-1, inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4, and transthyretin). The role of these proteins was discussed in relation to OC pathomechanism.
Conclusions: The study results may contribute to the development of clinically useful multi-component diagnostic tools in OC. In addition, identifying a novel panel of discriminative proteins could provide a new insight into complex signaling and functional networks associated with this multifactorial disease.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Epithelial ovarian cancer; MALDI-TOF; Ovarian cancer; Protein-peptide profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Bioethics Committee of Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland (Decision No. 165/16). All participants of the study signed informed consent to publish their (anonymized) data for scientific purposes.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Romagnolo C, Leon AE, Fabricio ASC, Taborelli M, Polesel J, Del Pup L, et al. HE4, CA125 and risk of ovarian malignancy algorithm (ROMA) as diagnostic tools for ovarian cancer in patients with a pelvic mass: an Italian multicenter study. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;141:303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.01.016. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous