Decreasing seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 in Germany leaves many people susceptible to genital infection: time to raise awareness and enhance control
- PMID: 28683784
- PMCID: PMC5500947
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2527-1
Decreasing seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 in Germany leaves many people susceptible to genital infection: time to raise awareness and enhance control
Abstract
Background: Herpes simplex infections (HSV1/2) are characterized by recurrent symptoms, a risk of neonatal herpes, and the facilitation of HIV transmission. In Germany, HSV1/2 infections are not notifiable and data are scarce. A previous study found higher HSV1/2 seroprevalences in women in East Germany than in women in West Germany. We assessed changes in the HSV1/2 seroprevalences over time and investigated determinants associated with HSV1/2 seropositivity to guide prevention and control.
Methods: The study was based on the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS; 2008-2011) and the German National Health Interview and Examination Survey (GNHIES; 1997-1999). We tested serum samples from DEGS participants for HSV1 and HSV2 immunoglobulin G. We used Pearson's χ2 test to compare the HSV1/HSV2 seroprevalences in terms of sex, age, and region of residence (East/West Germany) and investigated potential determinants by calculating prevalence ratios (PR) with log-binomial regression. All statistical analyses included survey weights.
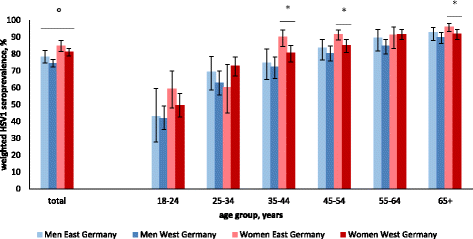
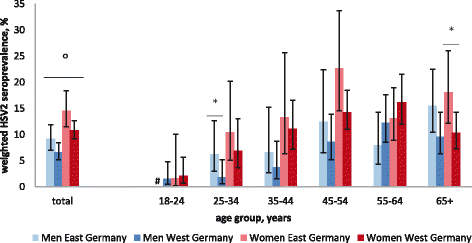
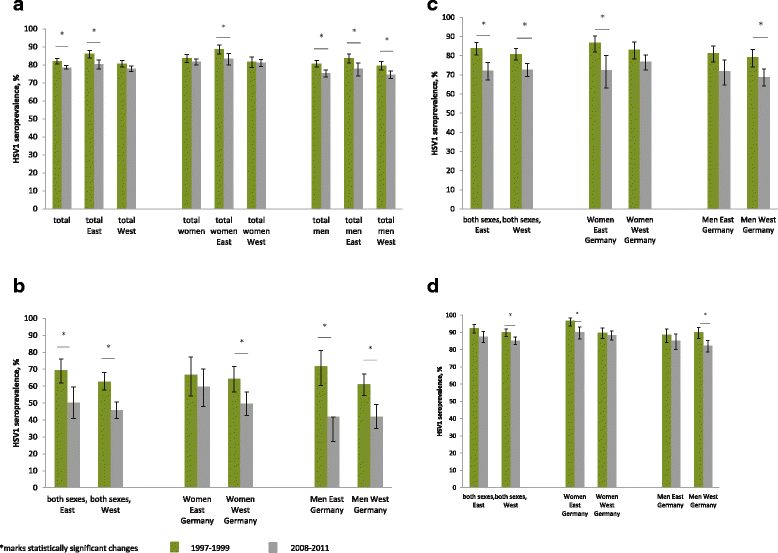
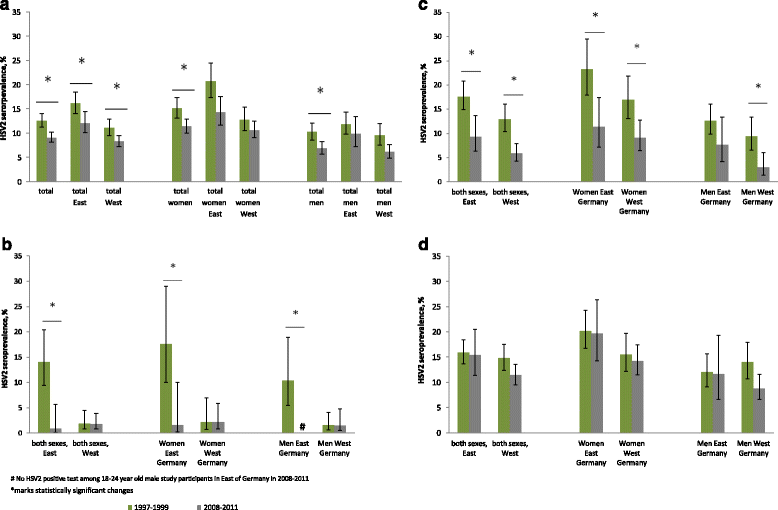
Results: In total, 6627 DEGS participants were tested for HSV1, and 5013 were also tested for HSV2. Overall, HSV1 seroprevalence decreased significantly from 1997-1999 (82.1%; 95%CI 80.6-83.6) to 2008-2011 (78.4%; 95%CI 77.8-79.7). In the same period, overall HSV2 seroprevalence decreased significantly from 13.3% (95%CI 11.9-14.9) to 9.6% (95%CI 8.6-10.8), notably in 18-24-year-old men (10.4 to 0%) in East Germany. Women were more likely than men to be seropositive for HSV1 (PR 1.1) or HSV2 (PR 1.6). A lower level of education, smoking, and not speaking German were associated with HSV1 in both sexes. Women of older age, who smoked, or had a history of abortion and men of older age or who had not attended a nursery school during childhood were more often seropositive for HSV2.
Conclusion: The reduced seroprevalences of HSV1 and HSV2 leave more people susceptible to genital HSV1/2 infections. Practitioners should be aware of HSV infection as a differential diagnosis for genital ulcers. We recommend educational interventions to raise awareness of the sexual transmission route of HSV1/2, possible consequences, and prevention. Interventions should especially target pregnant women, their partners, and people at risk of HIV.
Keywords: Germany; Health survey; Herpes genitalis; Herpes simplex; Seroepidemiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 in the Netherlands: seroprevalence, risk factors and changes during a 12-year period.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 2;16:364. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1707-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27484304 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence and correlates of herpes simplex virus type 2 infection among young adults in Arkhangelsk, Northwest Russia: a population-based cross-sectional study.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 28;16(1):616. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1954-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27793121 Free PMC article.
-
Ethnic differences in HSV1 and HSV2 seroprevalence in Amsterdam, the Netherlands.Euro Surveill. 2008 Jun 12;13(24):18904. Euro Surveill. 2008. PMID: 18761942
-
Epidemiology of genital herpes simplex virus infection in developed countries.Herpes. 2004 Apr;11 Suppl 1:2A-23A. Herpes. 2004. PMID: 15115626 Review.
-
[Natural history of HSV1 and HSV2 transmission modes and epidemiology consequences of HSV infection on HIV infection. Prevention].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002 Apr;129(4 Pt 2):571-6. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002. PMID: 12122326 Review. French.
Cited by
-
HSV-1 infection induces a downstream shift of the +1 nucleosome.J Virol. 2025 Apr 15;99(4):e0208624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02086-24. Epub 2025 Mar 25. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40130876 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 in Europe: systematic review, meta-analyses and meta-regressions.BMJ Glob Health. 2020 Jul;5(7):e002388. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-002388. BMJ Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 32675066 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese herbal prescription JZ-1 promotes extracellular vesicle production and protects against herpes simplex virus type 2 infection in vitro.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 5;10(5):e27019. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27019. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38495169 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Herpetic Activity of Killer Peptide (KP): An In Vitro Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 1;25(19):10602. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910602. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408931 Free PMC article.
-
Human in vivo evidence of associations between herpes simplex virus and cerebral amyloid-beta load in normal aging.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Apr 3;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01437-4. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38570885 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

