Evaluation of immune protection induced by DNA vaccines from Haemaphysalis longicornis paramyosin in rabbits
- PMID: 28683807
- PMCID: PMC5501075
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2262-x
Evaluation of immune protection induced by DNA vaccines from Haemaphysalis longicornis paramyosin in rabbits
Abstract
Background: Haemaphysalis longicornis is a blood-sucking ectoparasite that can cause diseases by transmitting some pathogens to humans and animals. Paramyosin (Pmy) is an immunomodulatory protein, which plays an important role in immune reactions against parasites. In this study, we evaluated the immune protection elicited by recombinant plasmids encoding H. longicornis Pmy in rabbits.
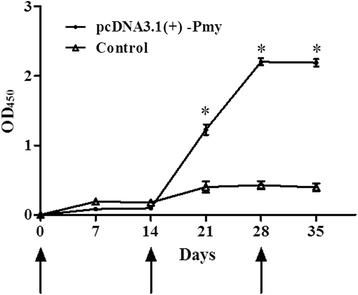
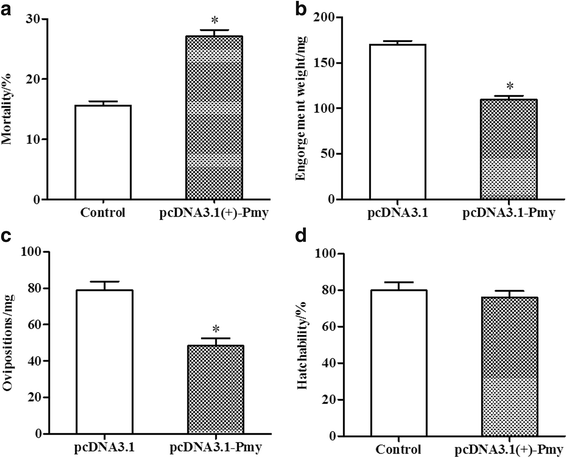
Results: Rabbits vaccinated with pcDNA3.1(+)-Pmy developed high level of IgG compared to control group, suggesting that humoral immune response was induced by vaccination. On the fourth day after fed on the rabbit, some female adults died and the mortality rate from pcDNA3.1(+)-Pmy group (27.31%) was significantly higher than that of the control group (P < 0.0001). Other female ticks were attached to the rabbits until detachment, and the average engorgement weight, oviposition of female adult from pcDNA3.1(+)-Pmy group were 109.61 ± 4.24 mg and 48.39 ± 4.06 mg, respectively, which correspondingly resulted in 36 and 39% reduction compared with that of the control group (P < 0.0001). In brief, vaccination with Pmy plasmid DNA provided an overall efficacy of 50% in immune protection of rabbits.
Conclusions: This study suggested that Pmy DNA vaccine can induce effective humoral immune response and partially protected rabbit against H. longicornis infection.
Keywords: DNA vaccine; Haemaphysalis longicornis; Immune protection; Pmy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animals did not undergo any additional blood sampling for this study. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Hebei Normal University as complying with the Animal protection law of the People’s Republic of China.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation on two types of paramyosin vaccines for the control of Haemaphysalis longicornis infestations in rabbits.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Jun 7;14(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04812-4. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34099029 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of anti-tick efficiency in rabbits induced by DNA vaccines encoding Haemaphysalis longicornis lipocalin homologue.Med Vet Entomol. 2022 Dec;36(4):511-515. doi: 10.1111/mve.12594. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Med Vet Entomol. 2022. PMID: 35801679
-
Subolesin vaccination inhibits blood feeding and reproduction of Haemaphysalis longicornis in rabbits.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Sep 18;13(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04359-w. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32948229 Free PMC article.
-
Biology, ecology and distribution of the tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis Neumann (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Zealand.N Z Vet J. 2016 Jan;64(1):10-20. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2015.1035769. Epub 2015 Jun 23. N Z Vet J. 2016. PMID: 25849758 Review.
-
Rabbits as Animal Models for Anti-Tick Vaccine Development: A Global Scenario.Pathogens. 2023 Sep 1;12(9):1117. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091117. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37764925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization and Expression Pattern of Paramyosin in Larvae and Adults of Yesso Scallop.Biology (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;11(3):453. doi: 10.3390/biology11030453. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336826 Free PMC article.
-
Ticks (Acari: Ixodoidea) in China: Geographical distribution, host diversity, and specificity.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019 Nov;102(3):e21544. doi: 10.1002/arch.21544. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30859631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular characterization and immune efficacy of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae).Parasit Vectors. 2023 May 25;16(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05794-1. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37231514 Free PMC article.
-
RBD and Spike DNA-Based Immunization in Rabbits Elicited IgG Avidity Maturation and High Neutralizing Antibody Responses against SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2023 Feb 17;15(2):555. doi: 10.3390/v15020555. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851769 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomics of the vector Dermacentor reticulatus revealed differentially regulated proteins associated with pathogen transmission in response to laboratory infection with Rickettsia slovaca.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jun 24;12(1):318. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3564-y. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31234913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee DW, Chang KS, Min JK, Ahn YJ, Jo HC, Kim SI. Acaricidal activity of commercialized insecticides against Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) nymphs. J Asia Pac Entomol. 2015;18:715–718. doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2015.09.004. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

