Effect of dextran-70 on outcome in severe sepsis; a propensity-score matching study
- PMID: 28683810
- PMCID: PMC5501466
- DOI: 10.1186/s13049-017-0413-x
Effect of dextran-70 on outcome in severe sepsis; a propensity-score matching study
Abstract
Background: Albumin may be beneficial in patients with septic shock but availability is limited and cost is high. The objective of the present study was to investigate if the use of dextran-70 in addition to albumin and crystalloids influences organ failure or mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock.
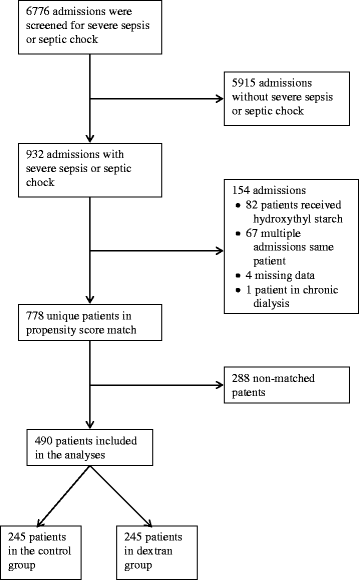
Methods: Patients with severe sepsis or septic shock (n = 778) admitted to a university hospital intensive care unit (ICU) between 2007 and 2015 that received dextran-70 during resuscitation were propensity score matched to controls at a 1 to 1 ratio. Outcomes were highest acute kidney injury network (AKIN) score the first 10 days in the ICU, use of renal replacement therapy, days alive and free of organ support the first 28 days after admission to ICU, mortality and events of severe bleeding. Outcomes were assessed using paired hypothesis testing.
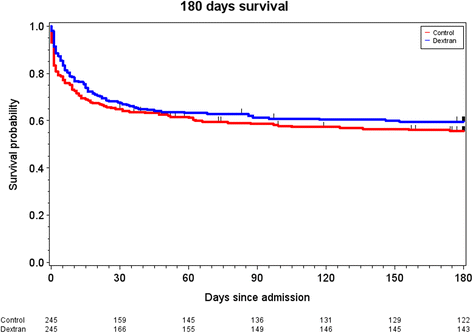
Results: Propensity score matching resulted in two groups of patients with 245 patients in each group. The dextran group received a median volume of 1483 ml (interquartile range, 1000-2000 ml) of dextran-70 during the ICU stay. Highest AKIN score did not differ between the control- and dextran groups (1 (0-3) versus 2 (0-3), p = 0.06). Incidence of renal replacement therapy in the control- and dextran groups was similar (19% versus 22%, p = 0.42, absolute risk reduction -2.9% [95% CI: -9.9 to 4.2]). Days alive and free of renal replacement, vasopressors and mechanical ventilation did not differ between the control- and dextran groups. The 180-day mortality was 50.2% in the control group and 41.6% in the dextran group (p = 0.046, absolute risk reduction 8.6% [-0.2 to 17.4]). Fraction of patients experiencing a severe bleeding in the first 10 days in the ICU did not differ between the control and dextran groups (14% versus 18%, p = 0.21).
Discussion: There is a paucity of high quality data regarding effects of dextran solutions on outcome in sepsis. In the present study, propensity score matching was used in attempt to reduce bias.
Conclusion: No evidence to support a detrimental effect of dextran-70 on mortality or on organ failures in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock could be detected.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Colloid; Crystalloid; Dextran; Resuscitation; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the regional ethical vetting board in Lund (registration number 2014/916).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar G, Walker E, Stephens R. Intravenous fluid therapy. Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care. 2014;4:55–59. doi: 10.1016/j.tacc.2014.04.005. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources