A novel ultra high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing library preparation method for the Illumina HiSeq platform
- PMID: 28683838
- PMCID: PMC5501495
- DOI: 10.1186/s40168-017-0279-1
A novel ultra high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing library preparation method for the Illumina HiSeq platform
Abstract
Background: Advances in sequencing technologies and bioinformatics have made the analysis of microbial communities almost routine. Nonetheless, the need remains to improve on the techniques used for gathering such data, including increasing throughput while lowering cost and benchmarking the techniques so that potential sources of bias can be better characterized.
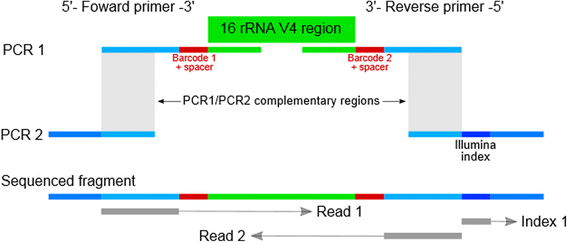
Methods: We present a triple-index amplicon sequencing strategy to sequence large numbers of samples at significantly lower c ost and in a shorter timeframe compared to existing methods. The design employs a two-stage PCR protocol, incorpo rating three barcodes to each sample, with the possibility to add a fourth-index. It also includes heterogeneity spacers to overcome low complexity issues faced when sequencing amplicons on Illumina platforms.
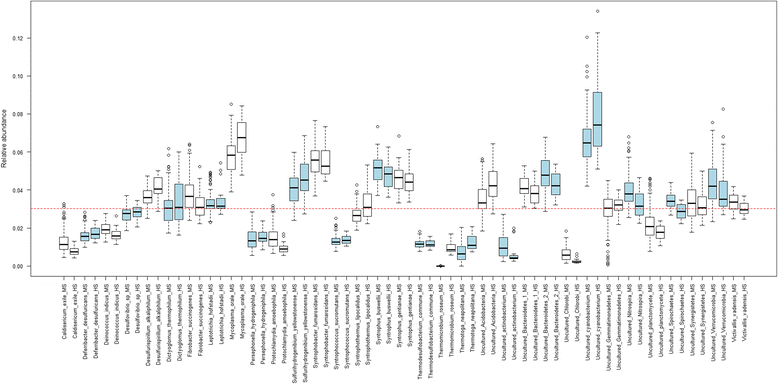
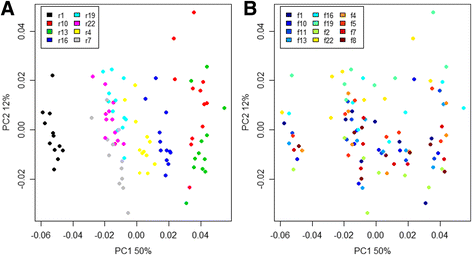
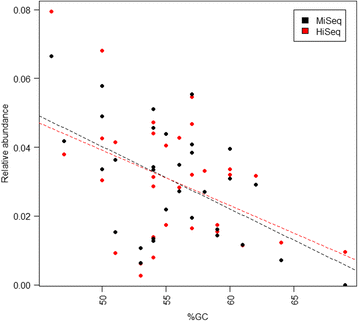
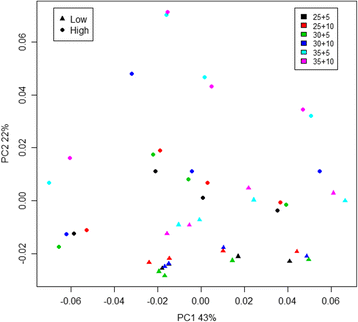
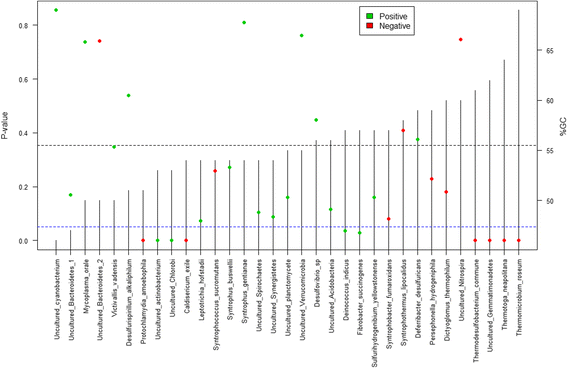
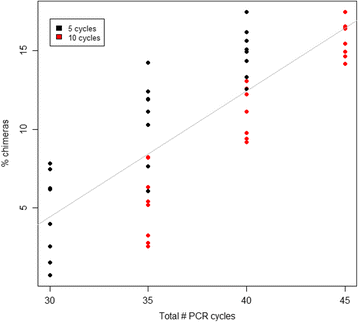
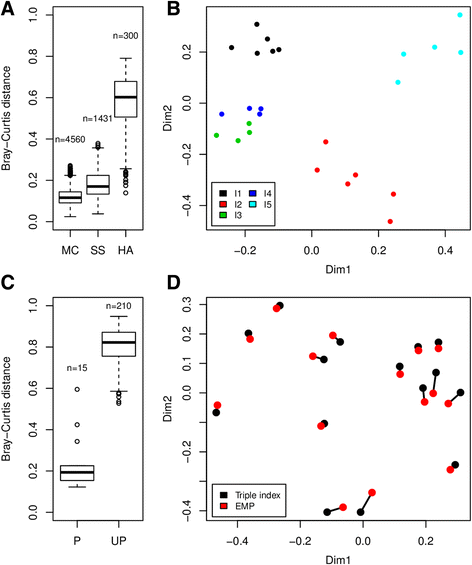
Results: The library preparation method was extensively benchmarked through analysis of a mock community in order to assess biases introduced by sample indexing, number of PCR cycles, and template concentration. We further evaluated the method through re-sequencing of a standardized environmental sample. Finally, we evaluated our protocol on a set of fecal samples from a small cohort of healthy adults, demonstrating good performance in a realistic experimental setting. Between-sample variation was mainly related to batch effects, such as DNA extraction, while sample indexing was also a significant source of bias. PCR cycle number strongly influenced chimera formation and affected relative abundance estimates of species with high GC content. Libraries were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms to demonstrate that this protocol is highly scalable to sequence thousands of samples at a very low cost.
Conclusions: Here, we provide the most comprehensive study of performance and bias inherent to a 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing method to date. Triple-indexing greatly reduces the number of long custom DNA oligos required for library preparation, while the inclusion of variable length heterogeneity spacers minimizes the need for PhiX spike-in. This design results in a significant cost reduction of highly multiplexed amplicon sequencing. The biases we characterize highlight the need for highly standardized protocols. Reassuringly, we find that the biological signal is a far stronger structuring factor than the various sources of bias.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing; Benchmarking; Chimera formation; Environmental sequencing; Illumina library preparation; Indexed PCR; Mock community; PCR bias.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-quality single amplicon sequencing method for illumina MiSeq platform using pool of 'N' (0-10) spacer-linked target specific primers without PhiX spike-in.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 23;24(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09233-4. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36959538 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of sequencing platforms and bioinformatics pipelines for compositional analysis of the gut microbiome.BMC Microbiol. 2017 Sep 13;17(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1101-8. BMC Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28903732 Free PMC article.
-
Improved pipeline for reducing erroneous identification by 16S rRNA sequences using the Illumina MiSeq platform.J Microbiol. 2015 Jan;53(1):60-9. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-4601-y. Epub 2015 Jan 4. J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25557481
-
Generating amplicon reads for microbial community assessment with next-generation sequencing.J Appl Microbiol. 2020 Feb;128(2):330-354. doi: 10.1111/jam.14380. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31299126 Review.
-
Best Practices for Illumina Library Preparation.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019 Jun;102(1):e86. doi: 10.1002/cphg.86. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31216112 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering CRISPR/Cas9 to mitigate abundant host contamination for 16S rRNA gene-based amplicon sequencing.Microbiome. 2020 Jun 3;8(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00859-0. Microbiome. 2020. PMID: 32493511 Free PMC article.
-
Coumarin biosynthesis genes are required after foliar pathogen infection for the creation of a microbial soil-borne legacy that primes plants for SA-dependent defenses.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 28;12(1):22473. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26551-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36577764 Free PMC article.
-
A collection of rumen bacteriome data from 334 mid-lactation dairy cows.Sci Data. 2019 Jan 22;6:180301. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.301. Sci Data. 2019. PMID: 30667380 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretations of Environmental Microbial Community Studies Are Biased by the Selected 16S rRNA (Gene) Amplicon Sequencing Pipeline.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 23;11:550420. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.550420. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33193131 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of probiotics on diversity and function of gut microbiota in Moschus berezovskii.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Aug;203(6):3305-3315. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02315-5. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33860850
References
-
- Low-diversity sequencing on the Illumina HiSeq platform (Illumina Technical Note 770-2014-035). Illumina. 2014. http://www.illumina.com/documents/products/technotes/technote-hiseq-low-... Accessed June 2016.
-
- Kozich JJ, Westcott SL, Baxter NT, Highlander SK, Schloss PD. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79:5112–20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01043-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

