BRAFV600 inhibition alters the microRNA cargo in the vesicular secretome of malignant melanoma cells
- PMID: 28684402
- PMCID: PMC5530690
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1705206114
BRAFV600 inhibition alters the microRNA cargo in the vesicular secretome of malignant melanoma cells
Abstract
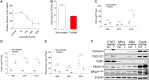
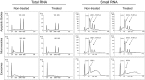
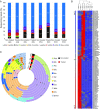
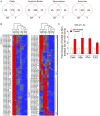
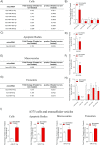
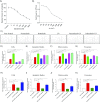
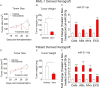
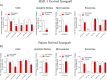
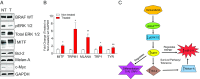
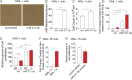
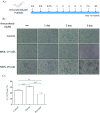
The BRAF inhibitors vemurafenib and dabrafenib can be used to treat patients with metastatic melanomas harboring BRAFV600 mutations. Initial antitumoral responses are often seen, but drug-resistant clones with reactivation of the MEK-ERK pathway soon appear. Recently, the secretome of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) has been ascribed important functions in cancers. To elucidate the possible functions of EVs in BRAF-mutant melanoma, we determined the RNA content of the EVs, including apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes, released from such cancer cells after vemurafenib treatment. We found that vemurafenib significantly increased the total RNA and protein content of the released EVs and caused significant changes in the RNA profiles. RNA sequencing and quantitative PCR show that cells and EVs from vemurafenib-treated cell cultures and tumor tissues harvested from cell-derived and patient-derived xenografts harbor unique miRNAs, especially increased expression of miR-211-5p. Mechanistically, the expression of miR-211-5p as a result of BRAF inhibition was induced by increased expression of MITF that regulates the TRPM1 gene resulting in activation of the survival pathway. In addition, transfection of miR-211 in melanoma cells reduced the sensitivity to vemurafenib treatment, whereas miR-211-5p inhibition in a vemurafenib resistant cell line affected the proliferation negatively. Taken together, our results show that vemurafenib treatment induces miR-211-5p up-regulation in melanoma cells both in vitro and in vivo, as well as in subsets of EVs, suggesting that EVs may provide a tool to understand malignant melanoma progression.
Keywords: cancer; extracellular vesicles; noncoding RNAs; small RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.L. has written several patents in the field of extracellular vesicles as therapeutics and is currently an employee of Codiak BioSciences, in parallel with his position at the University of Gothenburg. R.O.B. has received honoraria from Roche for lectures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma.Nat Commun. 2014 Dec 15;5:5712. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6712. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25502142 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription 3 sensitizes human cutaneous melanoma cells to BRAF inhibitor.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):67-77. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181365. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 30010109
-
p53 Reactivation by PRIMA-1(Met) (APR-246) sensitises (V600E/K)BRAF melanoma to vemurafenib.Eur J Cancer. 2016 Mar;55:98-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.12.002. Epub 2016 Jan 17. Eur J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26790143
-
The discovery of vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Sep;11(9):907-16. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1201057. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27327499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF mutant metastatic melanoma.Future Oncol. 2015;11(4):579-89. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.252. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25686114 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by melanoma exosome microRNA favours a pre-metastatic microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 27;8(1):12905. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31323-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30150674 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes, the message transporters in vascular calcification.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Sep;22(9):4024-4033. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13692. Epub 2018 Jun 12. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29892998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Melanoma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Impact on Melanoma Diagnosis, Progression Monitoring, and Treatment Response.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Dec 18;13(12):475. doi: 10.3390/ph13120475. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33353043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicle subpopulations from tissues.Nat Protoc. 2021 Mar;16(3):1548-1580. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-00466-1. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33495626
-
The Melanocyte Lineage Factor miR-211 Promotes BRAFV600E Inhibitor Resistance.J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Feb;141(2):250-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.07.010. J Invest Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33504438 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

