Integrated Assessment of Pharmacological and Nutritional Cardiovascular Risk Management: Blood Pressure Control in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT)
- PMID: 28684676
- PMCID: PMC5537824
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9070709
Integrated Assessment of Pharmacological and Nutritional Cardiovascular Risk Management: Blood Pressure Control in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT)
Abstract
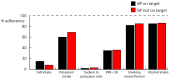
Cardiovascular risk management is an integral part of treatment in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), and requires pharmacological as well as nutritional management. We hypothesize that a systematic assessment of both pharmacological and nutritional management can identify targets for the improvement of treatment quality. Therefore, we analysed blood pressure (BP) management in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT). DIALECT is an observational cohort from routine diabetes care, performed at the ZGT Hospital (Almelo and Hengelo, The Netherlands). BP was measured for 15 minutes with one minute intervals. Sodium and potassium intake was derived from 24-hour urinary excretion. We determined the adherence to pharmacological and non-pharmacological guidelines in patients with BP on target (BP-OT) and BP not on target (BP-NOT). In total, 450 patients were included from August 2009 until January 2016. The mean age was 63 ± 9 years, and the majority was male (58%). In total, 53% had BP-OT. In those with BP-NOT, pharmacological management was suboptimal (zero to two antihypertensive drugs) in 62% of patients, and nutritional guideline adherence was suboptimal in 100% of patients (only 8% had a sodium intake on target, 66% had a potassium intake on target, 3% had a sodium-to-potassium ratio on target, and body mass index was <30 kg/m² in 35%). These data show pharmacological undertreatment and a low adherence to nutritional guidelines. Uncontrolled BP is common in T2DM, and our data show a window of opportunity for improving BP control, especially in nutritional management. To improve treatment quality, we advocate to incorporate the integrated monitoring of nutritional management in quality improvement cycles in routine care.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; blood pressure; dietary sodium intake; nutrition; pharmacological management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Real-life achievement of lipid-lowering treatment targets in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente: systemic assessment of pharmacological and nutritional factors.Nutr Diabetes. 2018 Apr 25;8(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s41387-018-0028-y. Nutr Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29695715 Free PMC article.
-
The future of antihypertensive treatment.Am J Ther. 2007 Mar-Apr;14(2):121-34. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000249915.12185.58. Am J Ther. 2007. PMID: 17414579 Review.
-
Salt intake in an urban, developing South African community.Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2006 Jul-Aug;17(4):186-91. Cardiovasc J S Afr. 2006. PMID: 17001421
-
Lifestyle modifications to prevent and control hypertension. 5. Recommendations on dietary salt. Canadian Hypertension Society, Canadian Coalition for High Blood Pressure Prevention and Control, Laboratory Centre for Disease Control at Health Canada, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada.CMAJ. 1999 May 4;160(9 Suppl):S29-34. CMAJ. 1999. PMID: 10333851 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:61-84. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_147. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27757935 Review.
Cited by
-
NT-proBNP Mediates the Association Between FGF23 and All-Cause Mortality in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Dec 5;12(23):e031873. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.031873. Epub 2023 Nov 28. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 38014662 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to Statin Therapy and Attainment of LDL Cholesterol Targets in an Outpatient Population of Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Analysis in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT).Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 12;13:888110. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.888110. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35903346 Free PMC article.
-
Glycaemic control in the diabetes and Lifestyle Cohort Twente: A cross-sectional assessment of lifestyle and pharmacological management on Hba1c target achievement.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Oct;20(10):2494-2499. doi: 10.1111/dom.13399. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29862616 Free PMC article.
-
Use of maximal dosage renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in a real life population of complicated type 2 diabetes - contraindications and opportunities.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Aug 16;24(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03205-2. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37587437 Free PMC article.
-
Body weight course in the DIAbetes and LifEstyle Cohort Twente (DIALECT-1)-A 20-year observational study.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 19;14(6):e0218400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218400. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31216324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Diabetes. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Langsted A., Freiberg J.J., Nordestgaard B.G. Extent of Undertreatment and Overtreatment with Cholesterol-Lowering Therapy According to European Guidelines in 92,348 Danes without Ischemic Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes in 2004–2014. Atherosclerosis. 2016;257:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.11.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Cosmo S., Viazzi F., Piscitelli P., Giorda C., Ceriello A., Genovese S., Russo G., Guida P., Fioretto P., Pontremoli R., et al. Blood Pressure Status and the Incidence of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Hypertens. 2016;34:2090–2098. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001045. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

