Multicolor spectral photon-counting computed tomography: in vivo dual contrast imaging with a high count rate scanner
- PMID: 28684756
- PMCID: PMC5500581
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04659-9
Multicolor spectral photon-counting computed tomography: in vivo dual contrast imaging with a high count rate scanner
Abstract
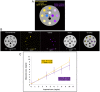
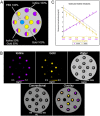
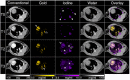
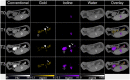
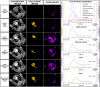
A new prototype spectral photon-counting computed tomography (SPCCT) based on a modified clinical CT system has been developed. SPCCT analysis of the energy composition of the transmitted x-ray spectrum potentially allows simultaneous dual contrast agent imaging, however, this has not yet been demonstrated with such a system. We investigated the feasibility of using this system to distinguish gold nanoparticles (AuNP) and an iodinated contrast agent. The contrast agents and calcium phosphate were imaged in phantoms. Conventional CT, gold K-edge, iodine and water images were produced and demonstrated accurate discrimination and quantification of gold and iodine concentrations in a phantom containing mixtures of the contrast agents. In vivo experiments were performed using New Zealand White rabbits at several times points after injections of AuNP and iodinated contrast agents. We found that the contrast material maps clearly differentiated the distributions of gold and iodine in the tissues allowing quantification of the contrast agents' concentrations, which matched their expected pharmacokinetics. Furthermore, rapid, repetitive scanning was done, which allowed measurement of contrast agent kinetics with high temporal resolution. In conclusion, a clinical scale, high count rate SPCCT system is able to discriminate gold and iodine contrast media in different organs in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
P.C., E.R., M.B., M.R., I.B. are employees of Philips Healthcare.
Figures

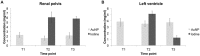
Similar articles
-
Improved Peritoneal Cavity and Abdominal Organ Imaging Using a Biphasic Contrast Agent Protocol and Spectral Photon Counting Computed Tomography K-Edge Imaging.Invest Radiol. 2018 Oct;53(10):629-639. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000483. Invest Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29794948 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution synchrotron K-edge subtraction CT allows tracking and quantifying therapeutic cells and their scaffold in a rat model of focal cerebral injury and can serve as a reference for spectral photon counting CT.Nanotheranostics. 2023 Jan 16;7(2):176-186. doi: 10.7150/ntno.79575. eCollection 2023. Nanotheranostics. 2023. PMID: 36793350 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of unconstrained three-material decomposition: imaging an excised human heart using a prototype silicon photon-counting CT detector.Eur Radiol. 2020 Nov;30(11):5904-5912. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07017-y. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32588212 Free PMC article.
-
First Experience With a Whole-Body Spectral Photon-Counting CT Clinical Prototype.Invest Radiol. 2023 Jul 1;58(7):459-471. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000965. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Invest Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36822663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles with "K-edge" Metals Bring "Color" in Multiscale Spectral Photon Counting X-ray Imaging.ACS Nano. 2024 Dec 24;18(51):34464-34491. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c11724. Epub 2024 Dec 9. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39652749 Review.
Cited by
-
Energy-integrating-detector multi-energy CT: Implementation and a phantom study.Med Phys. 2021 Sep;48(9):4857-4871. doi: 10.1002/mp.14943. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33988849 Free PMC article.
-
3D Spatial Distribution of Nanoparticles in Mice Brain Metastases by X-ray Phase-Contrast Tomography.Front Oncol. 2021 May 25;11:554668. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.554668. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34113554 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral Photon-Counting CT Technology in Chest Imaging.J Clin Med. 2021 Dec 9;10(24):5757. doi: 10.3390/jcm10245757. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34945053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-Source Photon-Counting Computed Tomography-Part III: Clinical Overview of Vascular Applications beyond Cardiac and Neuro Imaging.J Clin Med. 2023 May 31;12(11):3798. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113798. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37297994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of ultra-high-resolution photon-counting CT of bone metastases: initial experiences in breast cancer patients.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021 Jan 4;7(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00207-3. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33398008 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

