Does gastric bypass surgery change body weight set point?
- PMID: 28685029
- PMCID: PMC5485884
- DOI: 10.1038/ijosup.2016.9
Does gastric bypass surgery change body weight set point?
Abstract
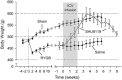
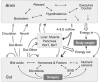
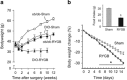
The relatively stable body weight during adulthood is attributed to a homeostatic regulatory mechanism residing in the brain which uses feedback from the body to control energy intake and expenditure. This mechanism guarantees that if perturbed up or down by design, body weight will return to pre-perturbation levels, defined as the defended level or set point. The fact that weight re-gain is common after dieting suggests that obese subjects defend a higher level of body weight. Thus, the set point for body weight is flexible and likely determined by the complex interaction of genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors. Unlike dieting, bariatric surgery does a much better job in producing sustained suppression of food intake and body weight, and an intensive search for the underlying mechanisms has started. Although one explanation for this lasting effect of particularly Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) is simple physical restriction due to the invasive surgery, a more exciting explanation is that the surgery physiologically reprograms the body weight defense mechanism. In this non-systematic review, we present behavioral evidence from our own and other studies that defended body weight is lowered after RYGB and sleeve gastrectomy. After these surgeries, rodents return to their preferred lower body weight if over- or underfed for a period of time, and the ability to drastically increase food intake during the anabolic phase strongly argues against the physical restriction hypothesis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain obscure. Although the mechanism involves central leptin and melanocortin signaling pathways, other peripheral signals such as gut hormones and their neural effector pathways likely contribute. Future research using both targeted and non-targeted 'omics' techniques in both humans and rodents as well as modern, genetically targeted, neuronal manipulation techniques in rodents will be necessary.
Conflict of interest statement
H-RB has received lecture fees from Novo Nordisk, and grant support from the National Institutes of Health. CDM and HM have also received grant support from the National Institutes of Health. JY has received grant support from Suntory Foundation. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
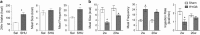
References
-
- Kennedy GC. The role of depot fat in the hypothalamic control of food intake in the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1953; 140: 578–596. - PubMed
-
- Keesey RE, Powley TL. Hypothalamic regulation of body weight. Am Sci 1975; 63: 558–565. - PubMed
-
- Wirtshafter D, Davis JD. Set points, settling points, and the control of body weight. Physiol Behav 1977; 19: 75–78. - PubMed
-
- Harris RB. Role of set-point theory in regulation of body weight. FASEB J 1990; 4: 3310–3318. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

