The level of serum carcinoembryonic antigen is a surrogate marker for the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs but is not an indication of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutationsm
- PMID: 28685062
- PMCID: PMC5492672
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2017.914
The level of serum carcinoembryonic antigen is a surrogate marker for the efficacy of EGFR-TKIs but is not an indication of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC patients with EGFR mutationsm
Abstract
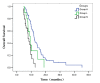
The aim of the present study was to define the relationship between carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients receiving epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and to investigate whether the level of serum CEA is related to the mechanism for acquisition of resistance to EGFR-TKIs. A total of 100 patients with advanced NSCLC (stage IIIB or stage IV) and harboring EGFR mutations were included. All patients received erlotinib or gefitinib treatment. The correlation between CEA serum level and clinical benefit from erlotinib or gefitinib treatment was analyzed. Patients were appraised by a review of data from a prospective re-biopsy protocol for lung cancer patients with an EGFR-mutated phenotype with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy. Of 100 patients, 49 and 21 patients carried high and low level of CEA, respectively; 30 carried normal CEA. Median progression-free survival was 6.4 and 4.5 months in patients with high and low level of CEA, respectively (P=0.027). Median PFS of patients in low-CEA group longer than that of those with normal level of tumors (3.0 months; P=0.002). The difference between groups L and N was not significant regarding objective response rate and overall survival. No significant difference was found in three groups of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs. The relative CEA level could predict benefit of EGFR-TKI therapy in advanced NSCLC, but could not predict acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: acquired drug resistances; carcinoembryonic antigen; epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokeratin 19 fragment predicts the efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutation.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Jul;8(7):892-8. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31828c3929. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23591159
-
[Serum CYFRA21-1 is Correlated with the Efficacy of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Harboring EGFR Mutations].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 Aug 20;19(8):550-8. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.08.12. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27561807 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prognostic and predictive value of serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor sensitive mutations and receiving tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 10;8(41):70865-70873. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20145. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050327 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of smoking status on progression-free and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib or gefitinib: a meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):661-71. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12332. Epub 2015 Nov 17. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26573867
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical impact of pleural fluid carcinoembryonic antigen on therapeutic strategy and efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma patients with malignant pleural effusion.Korean J Intern Med. 2024 Mar;39(2):318-326. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2023.309. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Korean J Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 38351680 Free PMC article.
-
The Prediction Of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation And Prognosis Of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor By Serum Ferritin In Advanced NSCLC.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Oct 7;11:8835-8843. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S216037. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31632143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–742. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et al. West Japan Oncology Group Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
