Increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a novel marker for nutrition, inflammation and chemotherapy outcome in patients with locally advanced and metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28685065
- PMCID: PMC5492691
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2017.924
Increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a novel marker for nutrition, inflammation and chemotherapy outcome in patients with locally advanced and metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
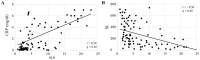
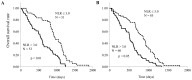
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common types of cancer, and its progression is strongly influenced by the presence of inflammation. Recently, there has been growing interest in the host inflammatory response, and increasing evidence has indicated that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), a useful marker of systemic inflammation, may be an effective prognostic indicator in various types of malignant diseases. In the present study, 260 patients with ESCC were enrolled, including 110 who received chemoradiation therapy (CRT) involving irradiation and chemotherapy of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin, and 150 received chemotherapy using 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin (FP). The patients of each group were both divided into two groups according to their NLR: High NLR (NLR>3.0) and low NLR (NLR≤3.0). Serum levels of prealbumin and retinol binding protein, which are nutritional parameters, were both significantly inversely correlated with NLR in patients treated with CRT, and patients treated with FP. Levels of CRP, a marker of inflammation, were significantly correlated with NLR, and stimulation indices, markers of immune reactions, were inversely correlated with NLR in both of CRT patients and FP patients. In patients treated with CRT, a partial response was significantly higher in patients with a low NLR and with progressive disease compared to those with a high NLR. In patients treated with FP, a partial response was also significantly higher in patients with a low NLR and with progressive disease compared to those with a high NLR. The overall survival of patients with CRT and FP were both significantly worse in patients with a high NLR than in those with a low NLR. NLR may serve as a useful marker of the tumor response, immune suppression, malnutrition and prognosis upon CRT or FP in patients with locally advanced or metastatic ESCC.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; inflammation; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; nutrition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with nutritional impairment, immune suppression, resistance to S-1 plus cisplatin, and poor prognosis in patients with stage IV gastric cancer.Mol Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;7(6):1073-1078. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1438. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Mol Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29285377 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker for patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 14;7:42581. doi: 10.1038/srep42581. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28195186 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of weekly docetaxel combined with preoperative radiotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer from pathological analysis.Dis Esophagus. 2014 May-Jun;27(4):368-73. doi: 10.1111/dote.12105. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Dis Esophagus. 2014. PMID: 23865505
-
Glasgow Prognostic Score as a Prognostic Clinical Marker in T4 Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):4897-901. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26254385
-
Combined neutrophil-platelet score and hemoglobin level predict survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with chemoradiotherapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 27;8(50):87971-87979. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21313. eCollection 2017 Oct 20. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29152134 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The clinical use of pretreatment NLR, PLR, and LMR in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: evidence from a meta-analysis.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Nov 22;10:6167-6179. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S171035. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30538564 Free PMC article.
-
Low skeletal muscle mass contributes to the prognosis of patients with superficial esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy.Esophagus. 2025 Apr;22(2):198-206. doi: 10.1007/s10388-025-01109-8. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Esophagus. 2025. PMID: 39883331
-
Clinical and prognostic significance of preoperative lymphocyte-monocyte ratio, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil-monocyte ratio on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Jun;9(6):3903-3914. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-2777. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117757 Free PMC article.
-
Gustave Roussy Immune Score (GRIm-Score) is a prognostic marker in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(6):1334-1340. doi: 10.7150/jca.37898. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32047540 Free PMC article.
-
Successful response to the combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy in cholangiocarcinoma with high tumour mutational burden and PD-L1 expression: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):1105. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5021-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30419854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaiswal M, LaRusso NF, Burgart LJ, Gores GJ. Inflammatory cytokines induce DNA damage and inhibit DNA repair in cholangiocarcinoma cells by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res. 2000;60:184–190. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
