Modified glasgow prognostic score in patients with small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28685088
- PMCID: PMC5492645
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1261
Modified glasgow prognostic score in patients with small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
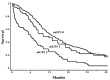
Systemic inflammatory response, which represents the presence of cachexia, is observed often in patients with lung cancer. To evaluate the prognostic significance of the presence of a systemic inflammatory response in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients, a retrospective study using modified Glasgow prognostic Score (mGPS) was performed. This score is composed of serum albumin and C-reactive protein levels. All the patients with SCLC who were diagnosed in Tsukuba University Hospital, Tsukuba Medical Center Hospital and Mito Medical Center between April 1999 and July 2016 were included in this study. During the study period, 332 patients with SCLC were consecutively admitted to these hospitals. Among them, 54 (16.9%) had mGPS=1, and 73 (22.9%) had mGPS=2. Male sex, advanced stage, poor performance status and no chemotherapy were unfavorable prognostic factors in uni- and multivariate-analysis. In addition, the presence of a systemic inflammatory response was confirmed as an unfavorable prognostic factor. In patients with SCLC, an existing systemic inflammatory response adversely affected the outcome. The patient's extent of disease as well as medical conditions including systemic inflammatory response must be taken into consideration when deciding whether to offer a standard therapy that may increase treatment-associated mortality.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; modified Glasgow prognostic score; serum albumin; small cell lung-cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Extensive Disease-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Study in a Single Institute.Chemotherapy. 2019;64(3):129-137. doi: 10.1159/000502681. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Chemotherapy. 2019. PMID: 31622969
-
Interstitial lung disease in patients with small cell lung cancer.Med Oncol. 2010 Sep;27(3):763-7. doi: 10.1007/s12032-009-9283-z. Epub 2009 Aug 6. Med Oncol. 2010. PMID: 19657749
-
Clinical utility of the modified Glasgow prognostic score in patients with advanced head and neck cancer.Head Neck. 2015 Dec;37(12):1745-9. doi: 10.1002/hed.23823. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Head Neck. 2015. PMID: 24989115
-
The value of the systematic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score in patients with gastric cancer: a literature review.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Oct-Dec;10(4):799-804. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.146054. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25579511 Review.
-
Prognostic Value of the Glasgow Prognostic Score or Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score for Patients with Colorectal Cancer Receiving Various Treatments: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1237-1249. doi: 10.1159/000495500. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30481755
Cited by
-
Glasgow prognostic score for prediction of chemotherapy-triggered acute exacerbation interstitial lung disease in patients with small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Jun;12(11):1681-1689. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13900. Epub 2021 May 3. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33939332 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Amrubicin Monotherapy as Second-Line Chemotherapy on Outcomes in Elderly Patients with Relapsed Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jun 23;12:4911-4921. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S255552. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32606979 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Morphological Phenotypes of COPD and Clinical Characteristics in Surgically Resected Patients with COPD and Concomitant Lung Cancer.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 Jun 21;17:1443-1452. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S366265. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 35761955 Free PMC article.
-
Change in Body Weight and Serum Albumin Levels in Febrile Neutropenic Lung Cancer Patients.Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2020;5(3):120-127. doi: 10.31372/20200503.1106. Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2020. PMID: 33324729 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of the cachexia index in patients with small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 17;21(1):563. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08300-x. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34001060 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous