Bilateral primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma without adrenal insufficiency: A case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 28685093
- PMCID: PMC5492831
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1264
Bilateral primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma without adrenal insufficiency: A case report and review of the literature
Abstract
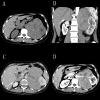
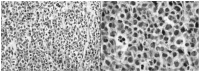
Primary adrenal lymphoma (PAL) is an infrequent malignant tumor, occurring in the bilateral adrenal glands as a mass in the majority of cases. The current study presents a case of bilateral primary adrenal diffuse large B cell lymphoma in a 52-year-old female patient, who presented with abdominal pain in the left lumbar region for ~2 weeks. Abdominal ultrasound examination and computed tomography scanning revealed a mass of 132×119×101 mm on the left adrenal gland and a mass of 53×27 mm on the right adrenal gland. A percutaneous biopsy was performed and histopathological examination further confirmed this lesion as diffuse large B cell lymphoma. The present study highlights the importance of early diagnosis of PAL, and performs a literature review of the subject.
Keywords: adrenal gland neoplasm; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; primary adrenal lymphoma.
Figures
References
-
- Mozos A, Ye H, Chuang WY, Chu JS, Huang WT, Chen HK, Hsu YH, Bacon CM, Du MQ, Campo E, Chuang SS. Most primary adrenal lymphomas are diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with non-germinal center B-cell phenotype, BCL6 gene rearrangement and poor prognosis. Mod Pathol. 2009;22:1210–1217. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.87. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
