Role of Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Inflammatory Arthritis
- PMID: 28685724
- PMCID: PMC5520561
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.209885
Role of Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) is a well-established imaging modality which has been put into clinical use in recent years with the development of second-generation contrast agent and imaging devices, and its applications in the assessment of inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, have provoked abundant discussion and researches among radiologists and rheumatologists. To summarize the achievements of clinical studies on CEUS in the application of arthritis, and to keep up with the latest progresses of the imaging technique, we reviewed the literature in recent years, hoping to establish the role of CEUS in joint diseases.
Data sources: PubMed and EMBASE.
Study selection: We searched the database with the conditions "contrast-enhanced ultrasound AND arthritis" with the time limitation of recent 10 years. Clinical studies applying CEUS in inflammatory arthritis and review articles about development of CEUS in joint diseases in English were selected.
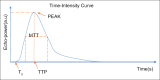
Results: As it is proved by most studies in recent years, by delineating microvasculature within the inflamed joints, CEUS can indicate early arthritis with high sensitivity and specificity. Moreover, the imaging of CEUS has been proved to be consistent with histopathological changes of inflammatory arthritis. Quantitative analysis of CEUS permits further evaluation of disease activity. CEUS also plays a significant role in the therapeutic monitoring of the disease, which has been backed up by a number of studies.
Conclusions: CEUS may be a new choice for the rheumatologists to evaluate inflammatory arthritis, because of its low price, ability to provide dynamic pictures, and high sensitivity to angiogenesis. It can also be applied in disease classification and therapeutic monitoring. More studies about CEUS need to be done to set up the diagnostic standards.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Carmona L, Wolfe F, Vos T, et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: Estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:1316–22. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204627. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8. - PubMed
-
- De Zordo T, Mlekusch SP, Feuchtner GM, Mur E, Schirmer M, Klauser AS. Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Radiol. 2007;64:222–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.07.011. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials