Understanding extreme sea levels for broad-scale coastal impact and adaptation analysis
- PMID: 28685752
- PMCID: PMC5504349
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms16075
Understanding extreme sea levels for broad-scale coastal impact and adaptation analysis
Abstract
One of the main consequences of mean sea level rise (SLR) on human settlements is an increase in flood risk due to an increase in the intensity and frequency of extreme sea levels (ESL). While substantial research efforts are directed towards quantifying projections and uncertainties of future global and regional SLR, corresponding uncertainties in contemporary ESL have not been assessed and projections are limited. Here we quantify, for the first time at global scale, the uncertainties in present-day ESL estimates, which have by default been ignored in broad-scale sea-level rise impact assessments to date. ESL uncertainties exceed those from global SLR projections and, assuming that we meet the Paris agreement goals, the projected SLR itself by the end of the century in many regions. Both uncertainties in SLR projections and ESL estimates need to be understood and combined to fully assess potential impacts and adaptation needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
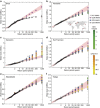

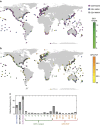
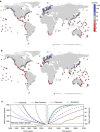
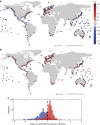
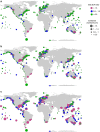
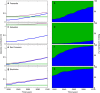
References
-
- Kron W. Coasts: the high-risk areas of the world. Nat. Hazards 66, 1363–1382 (2013).
-
- Church J. A. et al. in IPCC Climate Change 2013: the Physical Science Basis (eds Stocker T. F.et al. 1137–1216Cambridge University Press (2013).
-
- Wong P. P. et al. in IPCC Climate Change 2014: impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (eds Field C. B.et al. 361–409Cambridge University Press (2014).
-
- Hallegatte S., Green C., Nicholls R.J. & Corfee-Morlot J. Future flood losses in major coastal cities. Nat. Clim. Change 3, 802–806 (2013).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

