Enhanced opsonisation of Rhesus D-positive human red blood cells by recombinant polymeric immunoglobulin G anti-G antibodies
- PMID: 28686149
- PMCID: PMC5839618
- DOI: 10.2450/2017.0176-16
Enhanced opsonisation of Rhesus D-positive human red blood cells by recombinant polymeric immunoglobulin G anti-G antibodies
Abstract
Background: Anti-RhD antibodies (anti-D) are important in the prophylaxis of haemolytic disease of the foetus and newborn (HDFN) due to RhD incompatibility. Current preparations of anti-D are sourced from hyperimmune human plasma, so its production carries a risk of disease and is dependent on donor availability. Despite the efforts to develop a monoclonal preparation with similar prophylactic properties to the plasma-derived anti-D, no such antibody is yet available. Here we studied the agglutinating, opsonic and haemolytic activities of two recombinant polymeric immunoglobulins (Ig) against the G antigen of the Rh complex.
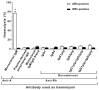
Materials and methods: Recombinant polymeric anti-G IgG1 (IgG1μtp) and IgG3 (IgG3μtp) were produced in vitro, purified by protein G-affinity chromatography, and analysed by gel electrophoresis. Their agglutinating, opsonic and haemolytic activities were evaluated using haemagglutination, erythrophagocytosis, and complement activation assays.
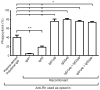
Results: The recombinant IgG1μtp and IgG3μtp anti-G antibodies ranged from 150,000 to 1,000,000 Da in molecular weight, indicating the formation of polymeric IgG. No complement activation or haemolytic activity was detected upon incubation of RhD-positive red-blood cells with the polymeric anti-G IgG. Both polymers were better opsonins than a prophylactic preparation of plasma-derived anti-D.
Discussion: The enhanced opsonic properties of the polymeric anti-G IgG1μtp and IgG3μtp could allow them to mediate the clearance of RhD-positive red blood cells from circulation more efficiently than natural or other synthetic prophylactic anti-D options. Their inability to induce complement-mediated haemolysis would be prophylactically convenient and is comparable in vitro to that of the available plasma-derived polyclonal anti-D preparations. The described properties suggest that polymeric antibodies like these (but with anti-D specificity) may be testable candidates for prophylaxis of HDFN caused by anti-D.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anstee DJ, Tanner MJA. Biochemical aspects of the blood group Rh (Rhesus) antigens. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1993;6:401–22. - PubMed
-
- Mollison PL, Engelfriet CP, Contreras M. The Rh blood group system (and LW) In: Klein HG, Anstee DJ, editors. Mollison’s Blood Transfusion in Clinical Medicine. 11th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2005. pp. 163–208.
-
- Kumpel BM. Efficacy of Rh(D) monoclonal antibodies in clinical trials as replacement therapy for prophylactic anti-D immunoglobulin: more questions than answers. Vox Sang. 2007;93:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Bowman J. Rh-immunoglobulin: Rh prophylaxis. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2006;19:27–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
