Increased levels of soluble forms of E-selectin and ICAM-1 adhesion molecules during human leptospirosis
- PMID: 28686648
- PMCID: PMC5501535
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180474
Increased levels of soluble forms of E-selectin and ICAM-1 adhesion molecules during human leptospirosis
Abstract
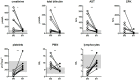
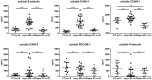
Leptospirosis is a multisystemic zoonotic disease with infiltration of visceral organs by Leptospira. The capacity of the vascular endothelium to grant immune cell recruitment and activation in target organs during the disease course remains poorly characterized. We ascertained the levels of expression of several soluble cell adhesion molecules (CAM) notably expressed by endothelial cells in human leptospirosis. We prospectively enrolled 20 hospitalized patients and compared them to 10 healthy controls. Disease severity was defined by one or more organ failures, or death. Plasmatic concentrations of soluble CAM were assessed by multiplex bead assay at the time of patient presentation (M0) and 1 month after hospital discharge. The levels of soluble E-selectin (sCD62E) and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (sICAM-1, sCD53) were significantly increased in patients compared to controls (p<0.0001) and at 1 month (p<0.0001) with median values at 978 ng/ml (interquartile ranges 787-1164; sCD62E) and 1021 ng/ml (690-1428; sCD53). At M0, Soluble P-selectin level (sCD62P) was found to be decreased with levels at 60 ng/ml (0-631) versus 711 ng/ml (343-1113) for healthy controls (p<0.05). Levels of sICAM-3 (sCD50), sVCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule, sCD106) and sPECAM-1 (platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule, sCD31) were not different from healthy subjects at M0. This study shows that two adhesion molecules, shed as soluble forms, are elevated during the acute phase of leptospirosis: E-selectin and s-ICAM1. These molecules may interfere with the process of immune cell recruitment to clear Leptospira at tissue levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 and CD146: soluble levels and in situ expression of cellular adhesion molecules implicated in the cohesion of endothelial cells in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies.J Rheumatol. 2006 Aug;33(8):1623-30. J Rheumatol. 2006. PMID: 16881117
-
Influence of age and dietary fish oil on plasma soluble adhesion molecule concentrations.Clin Sci (Lond). 2001 Jan;100(1):91-100. Clin Sci (Lond). 2001. PMID: 11115423 Clinical Trial.
-
Markers of endothelial cell activation and immune activation are increased in patients with severe leptospirosis and associated with disease severity.J Infect. 2015 Oct;71(4):437-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Infect. 2015. PMID: 26048204
-
Distinct accumulation patterns of soluble forms of E-selectin, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 upon infusion of TNFalpha in tumor patients.Thromb Haemost. 2003 Jun;89(6):1052-7. Thromb Haemost. 2003. PMID: 12783118
-
Soluble adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1) and selectins (sE selectin, sP selectin, sL selectin) levels in children and adolescents with obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.Metabolism. 2005 Aug;54(8):1020-6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2005.03.004. Metabolism. 2005. PMID: 16092051
Cited by
-
Association of markers of endothelial activation and dysfunction with occurrence and outcome of pulmonary hemorrhage in dogs with leptospirosis.J Vet Intern Med. 2021 Jul;35(4):1789-1799. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16163. Epub 2021 Jun 2. J Vet Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34076314 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Serum E-Selectin Levels Were Associated with Cognitive Decline in Patients with Stroke.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Mar 2;14:733-739. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S292171. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 33688244 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of microRNA-23b in patients with sepsis and its effect on leukocytes and the expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Dec;16(6):4707-4711. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6759. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30542424 Free PMC article.
-
Additive effect of erythropoietin use on exercise-induced endothelial activation and hypercoagulability in athletes.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020 Aug;120(8):1893-1904. doi: 10.1007/s00421-020-04419-0. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32537688 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The monocytosis during human leptospirosis is associated with modest immune cell activation states.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Oct;208(5):667-678. doi: 10.1007/s00430-018-0575-9. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30542761
References
-
- Costa F, Hagan JE, Calcagno J, Kane M, Torgerson P, Martinez-Silveira MS, et al. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9: e0003898 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003898 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levett PN. Leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001;14: 296–326. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.2.296-326.2001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adler B, editor. Leptospira and Leptospirosis [Internet]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; Berlin Heidelberg; 2015. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-662-45059-8 - DOI
-
- Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, et al. Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3: 757–771. - PubMed
-
- Fraga TR, Barbosa AS, Isaac L. Leptospirosis: aspects of innate immunity, immunopathogenesis and immune evasion from the complement system. Scand J Immunol. 2011;73: 408–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2010.02505.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

