Baccaurea angulata fruit juice reduces atherosclerotic lesions in diet-induced Hypercholesterolemic rabbits
- PMID: 28687076
- PMCID: PMC5501101
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0526-2
Baccaurea angulata fruit juice reduces atherosclerotic lesions in diet-induced Hypercholesterolemic rabbits
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis is the most common disease of large and medium-sized arteries linked to oxidative stress, dyslipidemia as well as chronic inflammation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the potential health benefits of Baccaurea angulata (BA) fruit juice on the aorta of diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rabbits, to detect an accumulation of fatty streak and evaluate the percentage of atherosclerotic lesion accrued.
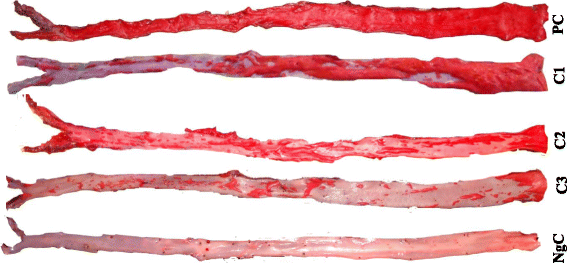
Methods: Thirty-five healthy male adults New Zealand White rabbits were assigned to seven different groups. Four groups were fed 1% cholesterol diet and 0, 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 mL of BA fruit juice per kg of rabbit daily (atherogenic groups), while the other three groups were fed commercial rabbit pellet and 0, 0.5, and 1.0 mL of juice per kg of rabbit daily (normocholesterolemic groups) for 90 days. The thoracic and abdominal aorta between the heart origin and bifurcation into iliac arteries of all the rabbits were carefully removed and analyzed accordingly.
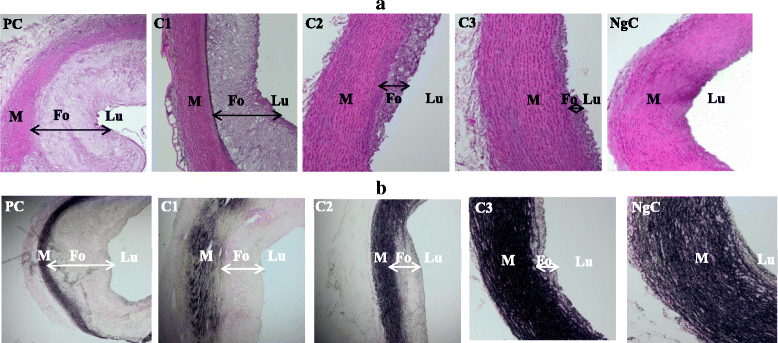
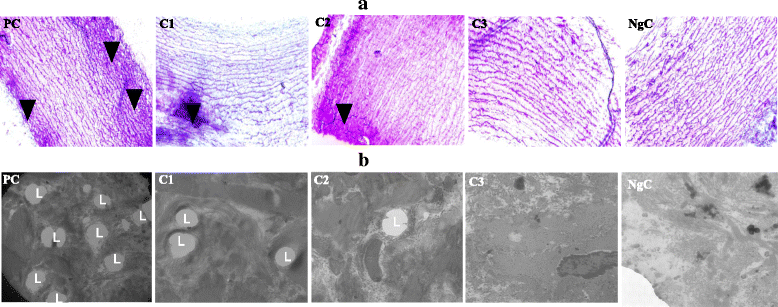
Results: The supplementation of the high-cholesterol diet of hypercholesterolemic rabbits with only 0.5 mL BA/kg rabbit per day significantly (p < 0.001) improved aortic lipid profile, attenuated aortic fatty streak development and reduced intima thickening. Higher BA doses used (1.0 and 1.5 mL/kg rabbit per day) also significantly (p < 0.001) decreased further the development of aortic fatty streaks, reduced the thickening of the tunica intima layer and preserved endothelial healing following arterial injury.
Conclusion: Therefore, BA fruit is a potential novel functional food with effective anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic and hypocholesterolemic activities.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Hypercholesterolemia; Intima thickness; Lesion; Lipid profile.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No human subject was used. All procedure and experimental protocols involved in animal handling were approved by the International Islamic University Malaysia (IIUM) Research Ethics Committee (IREC), Kulliyyah of Medicine, IIUM (ID NO.: IREC 04, Meeting No. 4/2012) and conformed to the guidelines of the Malaysian Code of Practice for the Care and Use of Animal for Scientific Purposes.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baccaurea angulata fruit juice ameliorates altered hematological and biochemical biomarkers in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rabbits.Nutr Res. 2017 Jun;42:31-42. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 May 5. Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 28633869
-
Comparison of the effects of three different Baccaurea angulata whole fruit juice doses on plasma, aorta and liver MDA levels, antioxidant enzymes and total antioxidant capacity.Eur J Nutr. 2018 Aug;57(5):1817-1828. doi: 10.1007/s00394-017-1466-3. Epub 2017 May 17. Eur J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 28516253
-
Baccaurea angulata fruit inhibits lipid peroxidation and induces the increase in antioxidant enzyme activities.Eur J Nutr. 2016 Jun;55(4):1435-44. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-0961-7. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26091909
-
Phenolic-Rich Baccaurea angulata Modulates Inflammatory Biomarkers of Atherosclerosis.J Nutr Metab. 2018 Nov 5;2018:8406193. doi: 10.1155/2018/8406193. eCollection 2018. J Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 30524759 Free PMC article.
-
Nikolaj Nikolajewitsch Anitschkow (1885-1964) established the cholesterol-fed rabbit as a model for atherosclerosis research.Atherosclerosis. 1997 Nov;135(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(97)00161-5. Atherosclerosis. 1997. PMID: 9395267 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends and challenges in phytotherapy and phytocosmetics for skin aging.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Aug;29(8):103363. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103363. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35813113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of CCL2, CCR5, ELMO1, and IL8 Polymorphism with Diabetic Nephropathy in Malaysian Type 2 Diabetic Patients.Int J Chronic Dis. 2019 Jan 1;2019:2053015. doi: 10.1155/2019/2053015. eCollection 2019. Int J Chronic Dis. 2019. PMID: 30713847 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical and antioxidant activity evaluation of the bark of Tampoi ( Baccaurea macrocarpa).F1000Res. 2018 Dec 24;7:1977. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.16643.2. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 31885857 Free PMC article.
-
CNDP1, NOS3, and MnSOD Polymorphisms as Risk Factors for Diabetic Nephropathy among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Malaysia.J Nutr Metab. 2019 Jan 3;2019:8736215. doi: 10.1155/2019/8736215. eCollection 2019. J Nutr Metab. 2019. PMID: 30719346 Free PMC article.
-
Static Magnetic Fields Modulate the Response of Different Oxidative Stress Markers in a Restraint Stress Model Animal.Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 14;2018:3960408. doi: 10.1155/2018/3960408. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29888261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morrison M, van der Heijden R, Heeringa P, Kaijzel E, Verschuren L, Blomhoff R, Kooistra T, Kleemann R. Epicatechin attenuates atherosclerosis and exerts anti-inflammatory effects on diet-induced human-CRP and NFκB in vivo. Atherosclerosis. 2014;233(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.12.027. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

