Reconstructing anatomy from electro-physiological data
- PMID: 28687516
- PMCID: PMC5725312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.06.049
Reconstructing anatomy from electro-physiological data
Abstract
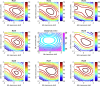
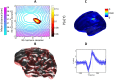
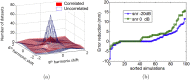
Here we show how it is possible to make estimates of brain structure based on MEG data. We do this by reconstructing functional estimates onto distorted cortical manifolds parameterised in terms of their spherical harmonics. We demonstrate that both empirical and simulated MEG data give rise to consistent and plausible anatomical estimates. Importantly, the estimation of structure from MEG data can be quantified in terms of millimetres from the true brain structure. We show, for simulated data, that the functional assumptions which are closer to the functional ground-truth give rise to anatomical estimates that are closer to the true anatomy.
Keywords: Brain anatomy; Fourier spherical harmonics; MEG/EEG brain imaging; Negative variational free energy.
Crown Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Baillet S., Mosher J., Leahy R. Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE signal Process. Mag. 2001;18(6):14–30.
-
- Chung M.K., Dalton K.M., Davidson R.J. Tensor-based cortical surface morphometry via weighted spherical harmonic representation. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging. August 2008;27(8):1143–1151. - PubMed
-
- Chung M.K., Dalton K.M., Shen L., Evans A.C., Davidson R.J. Weighted Fourier series representation and its application to quantifying the amount of gray matter. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging. April 2007;26(4):566–581. - PubMed
-
- Cootes T., Taylor C. Anatomical statistical models and their role in feature extraction. Br. J. Radiol. 2004;77(2):133–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

