Simultaneous GCaMP6-based fiber photometry and fMRI in rats
- PMID: 28687521
- PMCID: PMC5582003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.07.002
Simultaneous GCaMP6-based fiber photometry and fMRI in rats
Abstract
Background: Understanding the relationship between neural and vascular signals is essential for interpretation of functional MRI (fMRI) results with respect to underlying neuronal activity. Simultaneously measuring neural activity using electrophysiology with fMRI has been highly valuable in elucidating the neural basis of the blood oxygenation-level dependent (BOLD) signal. However, this approach is also technically challenging due to the electromagnetic interference that is observed in electrophysiological recordings during MRI scanning.
New method: Recording optical correlates of neural activity, such as calcium signals, avoids this issue, and has opened a new avenue to simultaneously acquire neural and BOLD signals.
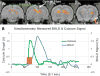
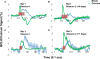
Results: The present study is the first to demonstrate the feasibility of simultaneously and repeatedly acquiring calcium and BOLD signals in animals using a genetically encoded calcium indicator, GCaMP6. This approach was validated with a visual stimulation experiment, during which robust increases of both calcium and BOLD signals in the superior colliculus were observed. In addition, repeated measurement in the same animal demonstrated reproducible calcium and BOLD responses to the same stimuli.
Comparison with existing method(s): Taken together, simultaneous GCaMP6-based fiber photometry and fMRI recording presents a novel, artifact-free approach to simultaneously measuring neural and fMRI signals. Furthermore, given the cell-type specificity of GCaMP6, this approach has the potential to mechanistically dissect the contributions of individual neuron populations to BOLD signal, and ultimately reveal its underlying neural mechanisms.
Conclusions: The current study established the method for simultaneous GCaMP6-based fiber photometry and fMRI in rats.
Keywords: Fiber photometry; GCaMP6; Rats; fMRI.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fiber-optic implant for simultaneous fluorescence-based calcium recordings and BOLD fMRI in mice.Nat Protoc. 2018 May;13(5):840-855. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2018.003. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29599439
-
Differential coupling between subcortical calcium and BOLD signals during evoked and resting state through simultaneous calcium fiber photometry and fMRI.Neuroimage. 2019 Oct 15;200:405-413. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31280011
-
Simultaneous BOLD fMRI and fiber-optic calcium recording in rat neocortex.Nat Methods. 2012 Jun;9(6):597-602. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2013. Epub 2012 May 6. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22561989
-
Multimodal Functional Neuroimaging by Simultaneous BOLD fMRI and Fiber-Optic Calcium Recordings and Optogenetic Control.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Apr;20(2):171-182. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1130-6. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 29027094 Review.
-
The neural basis of the blood-oxygen-level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging signal.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002 Aug 29;357(1424):1003-37. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2002.1114. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12217171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deriving causal relationships in resting-state functional connectivity using SSFO-based optogenetic fMRI.J Neural Eng. 2022 Nov 8;19(6):10.1088/1741-2552/ac9d66. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac9d66. J Neural Eng. 2022. PMID: 36301683 Free PMC article.
-
Global brain signal in awake rats.Brain Struct Funct. 2020 Jan;225(1):227-240. doi: 10.1007/s00429-019-01996-5. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2020. PMID: 31802256 Free PMC article.
-
Acute alcohol induces greater dose-dependent increase in the lateral cortical network functional connectivity in adult than adolescent rats.Addict Neurosci. 2023 Sep;7:100105. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2023.100105. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Addict Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37576436 Free PMC article.
-
Computing hemodynamic response functions from concurrent spectral fiber-photometry and fMRI data.Neurophotonics. 2022 Jul;9(3):032205. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.3.032205. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Neurophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35005057 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo localization of chronically implanted electrodes and optic fibers in mice.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 17;11(1):4686. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18472-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32943633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan KC, Xing KK, Cheung MM, Zhou IY, Wu EX. Functional MRI of postnatal visual development in normal and hypoxic-ischemic-injured superior colliculi. Neuroimage. 2010;49:2013–20. - PubMed
-
- Genovese CR, Lazar NA, Nichols T. Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. Neuroimage. 2002;15:870–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

