Reduced threshold for store overload-induced Ca2+ release is a common defect of RyR1 mutations associated with malignant hyperthermia and central core disease
- PMID: 28687594
- PMCID: PMC5803747
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20170282
Reduced threshold for store overload-induced Ca2+ release is a common defect of RyR1 mutations associated with malignant hyperthermia and central core disease
Abstract
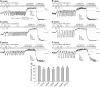
Mutations in the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor (RyR1) cause malignant hyperthermia (MH) and central core disease (CCD), whereas mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) lead to catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT). Most disease-associated RyR1 and RyR2 mutations are located in the N-terminal, central, and C-terminal regions of the corresponding ryanodine receptor (RyR) isoform. An increasing body of evidence demonstrates that CPVT-associated RyR2 mutations enhance the propensity for spontaneous Ca2+ release during store Ca2+ overload, a process known as store overload-induced Ca2+ release (SOICR). Considering the similar locations of disease-associated RyR1 and RyR2 mutations in the RyR structure, we hypothesize that like CPVT-associated RyR2 mutations, MH/CCD-associated RyR1 mutations also enhance SOICR. To test this hypothesis, we determined the impact on SOICR of 12 MH/CCD-associated RyR1 mutations E2347-del, R2163H, G2434R, R2435L, R2435H, and R2454H located in the central region, and Y4796C, T4826I, L4838V, A4940T, G4943V, and P4973L located in the C-terminal region of the channel. We found that all these RyR1 mutations reduced the threshold for SOICR. Dantrolene, an acute treatment for MH, suppressed SOICR in HEK293 cells expressing the RyR1 mutants R164C, Y523S, R2136H, R2435H, and Y4796C. Interestingly, carvedilol, a commonly used β-blocker that suppresses RyR2-mediated SOICR, also inhibits SOICR in these RyR1 mutant HEK293 cells. Therefore, these results indicate that a reduced SOICR threshold is a common defect of MH/CCD-associated RyR1 mutations, and that carvedilol, like dantrolene, can suppress RyR1-mediated SOICR. Clinical studies of the effectiveness of carvedilol as a long-term treatment for MH/CCD or other RyR1-associated disorders may be warranted.
Keywords: Ca2+ overload; calcium release; disease mutation; malignant hyperthermia; ryanodine receptor; sarcoplasmic reticulum.
© 2017 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



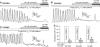


Similar articles
-
Reduced threshold for luminal Ca2+ activation of RyR1 underlies a causal mechanism of porcine malignant hyperthermia.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):20813-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801944200. Epub 2008 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18505726 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations of Malignant Hyperthermia and Central Core Disease Mutations in the Central Region of the RYR1 Channel.Hum Mutat. 2016 Nov;37(11):1231-1241. doi: 10.1002/humu.23072. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Hum Mutat. 2016. PMID: 27586648
-
Distinct effects on Ca2+ handling caused by malignant hyperthermia and central core disease mutations in RyR1.Biophys J. 2004 Nov;87(5):3193-204. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048447. Epub 2004 Sep 3. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 15347586 Free PMC article.
-
Ryanodine receptor mutations in malignant hyperthermia and central core disease.Hum Mutat. 2000;15(5):410-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200005)15:5<410::AID-HUMU2>3.0.CO;2-D. Hum Mutat. 2000. PMID: 10790202 Review.
-
Mutations in RYR1 in malignant hyperthermia and central core disease.Hum Mutat. 2006 Oct;27(10):977-89. doi: 10.1002/humu.20356. Hum Mutat. 2006. PMID: 16917943 Review.
Cited by
-
Cored in the act: the use of models to understand core myopathies.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Dec 19;12(12):dmm041368. doi: 10.1242/dmm.041368. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 31874912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding the ryanodine receptor calcium release channels and their role in calcium signalling.F1000Res. 2018 Nov 27;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1851. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.16434.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30542613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+ Channels Mediate Bidirectional Signaling between Sarcolemma and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum in Muscle Cells.Cells. 2019 Dec 24;9(1):55. doi: 10.3390/cells9010055. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31878335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective ryanodine receptor N-terminus inter-subunit interaction is a common mechanism in neuromuscular and cardiac disorders.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 12;13:1032132. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1032132. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36311249 Free PMC article.
-
Ryanodine Receptor 1-Related Myopathies: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches.Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Oct;15(4):885-899. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-00677-1. Neurotherapeutics. 2018. PMID: 30406384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

