Assessment of the protein interaction between coagulation factor XII and corn trypsin inhibitor by molecular docking and biochemical validation
- PMID: 28688220
- PMCID: PMC5638086
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.13773
Assessment of the protein interaction between coagulation factor XII and corn trypsin inhibitor by molecular docking and biochemical validation
Abstract
Essentials Corn Trypsin Inhibitor (CTI) is a selective inhibitor of coagulation Factor XII (FXII). Molecular modelling of the CTI-FXIIa complex suggested a canonical inhibitor binding mode. Mutagenesis revealed the CTI inhibitory loop and helices α1 and α2 mediate the interaction. This confirms that CTI inhibits FXII in canonical fashion and validates the molecular model.
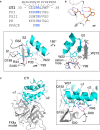
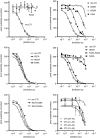
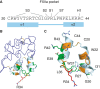
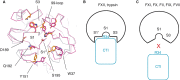
Summary: Background Corn trypsin inhibitor (CTI) has selectivity for the serine proteases coagulation factor XII and trypsin. CTI is in widespread use as a reagent that specifically inhibits the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation but not the extrinsic pathway. Objectives To investigate the molecular basis of FXII inhibition by CTI. Methods We performed molecular docking of CTI, using its known crystal structure, with a model of the activated FXII (FXIIa) protease domain. The interaction model was verified by use of a panel of recombinant CTI variants tested for their ability to inhibit FXIIa enzymatic activity in a substrate cleavage assay. Results The docking predicted that: (i) the CTI central inhibitory loop P1 Arg34 side chain forms a salt bridge with the FXIIa S1 pocket Asp189 side chain; (ii) Trp22 from CTI helix α1 interacts with the FXIIa S3 pocket; and (iii) Arg43 from CTI helix α2 forms a salt bridge with FXIIa H1 pocket Asp60A. CTI amino acid substitution R34A negated all inhibitory activity, whereas the G32W, L35A, W22A and R42A/R43A substitutions reduced activity by large degrees of 108-fold, 41-fold, 158-fold, and 100-fold, respectively; the R27A, W37A, W39A and R42A substitutions had no effect. Synthetic peptides spanning CTI residues 20-44 had inhibitory activity that was three-fold to 4000-fold less than that of full-length CTI. Conclusions The data confirm the validity of a canonical model of the FXIIa-CTI interaction, with helix α1 (Trp22), central inhibitory loop (Arg34) and helix α2 (Arg43) of CTI being required for effective binding by contacting the S1, S3 and H1 pockets of FXIIa, respectively.
Keywords: corn trypsin inhibitor; factor XII; molecular docking simulation; serine protease; trypsin.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactions outside the proteinase-binding loop contribute significantly to the inhibition of activated coagulation factor XII by its canonical inhibitor from corn.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 16;289(20):14109-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553735. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24706752 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation factor XII protease domain crystal structure.J Thromb Haemost. 2015 Apr;13(4):580-91. doi: 10.1111/jth.12849. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Thromb Haemost. 2015. PMID: 25604127 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of corn trypsin inhibitor and inhibiting antibodies for FXIa and FXIIa on coagulation of plasma and whole blood.J Thromb Haemost. 2014 Oct;12(10):1678-86. doi: 10.1111/jth.12707. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25142753
-
Factor XII/XIIa inhibitors: Their discovery, development, and potential indications.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 15;208:112753. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112753. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32883641 Review.
-
Structure-function relationship of serine protease-protein inhibitor interaction.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(2):419-28. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11732612 Review.
Cited by
-
Factor XII Activation Promotes Platelet Consumption in the Presence of Bacterial-Type Long-Chain Polyphosphate In Vitro and In Vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Aug;38(8):1748-1760. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311193. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 30354195 Free PMC article.
-
An update on factor XI structure and function.Thromb Res. 2018 Jan;161:94-105. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Thromb Res. 2018. PMID: 29223926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contact Pathway Function During Human Whole Blood Clotting on Procoagulant Surfaces.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Jul 23;5:209. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00209. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30083534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil α-defensins promote thrombosis in vivo by altering fibrin formation, structure, and stability.Blood. 2019 Jan 31;133(5):481-493. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-07-861237. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30442678 Free PMC article.
-
6-(Arylaminomethyl) Isoquinolines as Enzyme Inhibitors and Their Preparation: A Patent Highlight of Factor XIIa Inhibitors.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023;21(3):243-249. doi: 10.2174/1871525721666230126114224. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36703578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henriques ES, Floriano WB, Reuter N, Melo A, Brown D, Gomes JANF, Maigret B, Nascimento MAC, Ramos MJ. The search for a new model structure of b‐Factor XIIa. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2001; 15: 309–22. - PubMed
-
- Citarella F, Ravon DM, Pascucci B, Felici A, Fantoni A, Hack CE. Structure/function analysis of human factor XII using recombinant deletion mutants. Evidence for an additional region involved in the binding to negatively charged surfaces. Eur J Biochem 1996; 238: 240–9. - PubMed
-
- Iwaki T, Castellino FJ. Plasma levels of bradykinin are suppressed in factor XII‐deficient mice. Thromb Haemost 2006; 95: 1003–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

