Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes in U.S. Hispanic Youth: A Systematic Review of Lifestyle Interventions
- PMID: 28688727
- PMCID: PMC5610076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2017.05.020
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes in U.S. Hispanic Youth: A Systematic Review of Lifestyle Interventions
Abstract
Context: Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in youth has increased rapidly in recent decades along with rises in childhood obesity. Disparities in risk and prevalence of T2DM are evident in Hispanic youth when compared with non-Hispanic whites. Targeted diabetes prevention programs have been recommended to reduce risk prior to adulthood in this population. This systematic review explores the effectiveness of lifestyle-based diabetes prevention interventions for Hispanic youth.
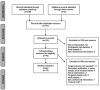
Evidence acquisition: PubMed, PsycINFO, Web of Science, and CENTRAL were searched from database inception to March 1, 2017, for studies that evaluated lifestyle-focused prevention trials targeting U.S. Hispanic youth under age 18 years. Fifteen publications met criteria for inclusion.
Evidence synthesis: Of the 15 studies, 11 were RCTs; four were uncontrolled. Interventions were heterogeneous in intensity, content, and setting. Duration of most trials was 12-16 weeks. Mean age of participants ranged from 9.8 to 15.8 years, sample sizes were generally small, and the majority of participants were overweight (BMI ≥85th percentile). Three studies reported statistically significant reductions in mean BMI, four in BMI z-score, and six in fasting glucose/insulin. Study quality was moderate to high. Effect sizes were generally small to medium.
Conclusions: Evidence for the impact of lifestyle-based diabetes prevention interventions targeting U.S. Hispanic youth remains limited. Few interventions demonstrated success in reducing BMI and glucose regulation and follow-up times were brief. More studies are needed that recruit larger samples sizes, extend follow-up times, explore innovative delivery modalities, and examine effectiveness across sex and age.
Copyright © 2017 American Journal of Preventive Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetes Prevention in U.S. Hispanic Adults: A Systematic Review of Culturally Tailored Interventions.Am J Prev Med. 2017 Apr;52(4):519-529. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2016.10.028. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Am J Prev Med. 2017. PMID: 27989451 Free PMC article.
-
Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of women with gestational diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 4;5(5):CD011970. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011970.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28472859 Free PMC article.
-
Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children from the age of 6 to 11 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD012651. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012651. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28639319 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of Facilitators and Barriers of Healthy Living and Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Among Latinx Families.J Lat Psychol. 2022 Aug;10(3):225-240. doi: 10.1037/lat0000205. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Lat Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36211633 Free PMC article.
-
Sex as a moderator of body composition following a randomized controlled lifestyle intervention among Latino youth with obesity.Pediatr Obes. 2020 Jun;15(6):e12620. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12620. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Pediatr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32072749 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lifestyle Modification Programs and Interventions on Prediabetes in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Scoping Review.J Prev (2022). 2025 Aug;46(4):615-637. doi: 10.1007/s10935-025-00835-0. Epub 2025 Apr 11. J Prev (2022). 2025. PMID: 40216730
-
Perceptions of Family-Level Social Factors That Influence Health Behaviors in Latinx Adolescents and Young Adults at High Risk for Type 2 Diabetes.Children (Basel). 2021 May 18;8(5):406. doi: 10.3390/children8050406. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069897 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Moderates Treatment Effects of Integrated Collaborative Care for Comorbid Obesity and Depression: The RAINBOW RCT.Ann Behav Med. 2021 Nov 18;55(12):1157-1167. doi: 10.1093/abm/kaaa125. Ann Behav Med. 2021. PMID: 33616188 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. Acute and chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Lancet. 2007;369(9575):1823–1831. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60821–6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Isasi CR, Parrinello CM, Ayala GX, et al. Sex Differences in Cardiometabolic Risk Factors among Hispanic/Latino Youth. J Pediatr. 2016;176:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.05.037. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dabelea D, Mayer-Davis EJ, Saydah S, et al. Prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among children and adolescents from 2001 to 2009. JAMA. 2014;311(17):1778–1786. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3201. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Lawman HG, et al. Trends in Obesity Prevalence Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 1988-1994 Through 2013-2014. JAMA. 2016;315(21):2292–2299. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.6361. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson WD, Kroon JJM, Greenway FL, Bouchard C, Ryan DH, Katzmarzyk PT. Prevalence of risk factors for metabolic syndrome in adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001-2006. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009;163(4):373–377. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous