Early Hearing Detection and Vocabulary of Children With Hearing Loss
- PMID: 28689189
- PMCID: PMC5595069
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-2964
Early Hearing Detection and Vocabulary of Children With Hearing Loss
Abstract
Background and objectives: To date, no studies have examined vocabulary outcomes of children meeting all 3 components of the Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) guidelines (hearing screening by 1 month, diagnosis of hearing loss by 3 months, and intervention by 6 months of age). The primary purpose of the current study was to examine the impact of the current EHDI 1-3-6 policy on vocabulary outcomes across a wide geographic area. A secondary goal was to confirm the impact of other demographic variables previously reported to be related to language outcomes.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study of 448 children with bilateral hearing loss between 8 and 39 months of age (mean = 25.3 months, SD = 7.5 months). The children lived in 12 different states and were participating in the National Early Childhood Assessment Project.
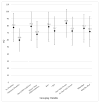
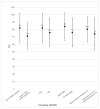
Results: The combination of 6 factors in a regression analysis accounted for 41% of the variance in vocabulary outcomes. Vocabulary quotients were significantly higher for children who met the EHDI guidelines, were younger, had no additional disabilities, had mild to moderate hearing loss, had parents who were deaf or hard of hearing, and had mothers with higher levels of education.
Conclusions: Vocabulary learning may be enhanced with system improvements that increase the number of children meeting the current early identification and intervention guidelines. In addition, intervention efforts need to focus on preventing widening delays with chronological age, assisting mothers with lower levels of education, and incorporating adults who are deaf/hard-of-hearing in the intervention process.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) [Accessed February 12, 2017];Effects of hearing loss on development. Available at: www.asha.org/public/hearing/effects-of-hearing-loss-on-development.
-
- Nott P, Cowan R, Brown PM, Wigglesworth G. Early language development in children with profound hearing loss fitted with a device at a young age: part I–the time period taken to acquire first words and first word combinations. Ear Hear. 2009;30(5):526–540. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):898–921. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

