Neuroprotective Effects of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylserine Against Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells
- PMID: 28689275
- PMCID: PMC11481886
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-017-0516-y
Neuroprotective Effects of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylserine Against Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells
Abstract
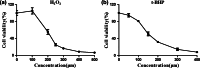
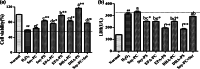
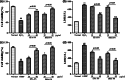
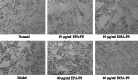
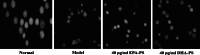
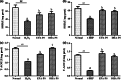
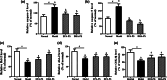
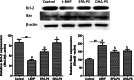
Neurodegenerative diseases are defined by progressive loss of specific neuronal cell populations and are associated with protein aggregates. Oxidative stress has been implicated in their pathological processes. Previous studies revealed that docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases. Phospholipids (PLs) derived from marine products are rich in DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). In the present study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of DHA-enriched and unenriched phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) on oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and tert-butylhydroperoxide in PC12 cells. Cell viability and leakage of lactate dehydrogenase results showed that the neuroprotective effect of PS was superior to that of PC. DHA- and EPA-enriched PC and PS were superior to that without DHA or EPA; in addition, the improvement with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched PS (n-3 PS) was dose dependent. Acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining showed that DHA- and EPA-enriched PS (DHA/EPA-PS) could significantly inhibit apoptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that EPA-PS and DHA-PS were effective to increase superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels by 48.4 and 58.2 % and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) level by 51 and 94 %, respectively, in the H2O2 model. Similar results for SOD and T-AOC levels were shown in the t-BHP model. EPA/DHA-PS could downregulate the messenger RNA level of Caspase-3, Caspase-9, and Bax, upregulate Bcl-2, inhibit Bax, and increase Bcl-2 at protein level. In conclusion, EPA/DHA-PS could protect PC12 cells from oxidative stress and prevent mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis. Our findings indicate that the neuroprotective effects of DHA/EPA-PLs depend on the molecular form. Further studies are necessary to reveal detailed mechanisms and structure-effect relationships.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis; Oxidative stress; n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched phosphatidylserine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
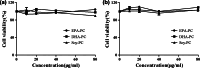
Similar articles
-
The protective effect of eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids from sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa on oxidative stress in PC12 cells and SAMP8 mice.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.10.015. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24231470
-
A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jul 19;21(7):410. doi: 10.3390/md21070410. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37504941 Free PMC article.
-
DHA protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress and apoptotic signals through the activation of the NFE2L2/HO-1 axis.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Jun;43(6):2523-2531. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4170. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31017264
-
YGS40, an active fraction of Yi-Gan San, reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells.Chin J Nat Med. 2015 Jun;13(6):438-44. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30037-6. Chin J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26073340
-
Phosphatidylserine in the brain: metabolism and function.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Oct;56:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 30. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24992464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspectives on lecithin from egg yolk: Extraction, physicochemical properties, modification, and applications.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 6;9:1082671. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1082671. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36687715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Egg Yolk and Soybean Phospholipids on Hepatic Fatty Acid Profile and Liver Protection in Rats Fed a High-Fructose Diet.Foods. 2021 Jul 6;10(7):1569. doi: 10.3390/foods10071569. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34359438 Free PMC article.
-
Antarctic krill oil exhibited synergistic effects with nobiletin and theanine in ameliorating memory and cognitive deficiency in SAMP8 mice: Applying the perspective of the sea-land combination to retard brain aging.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Sep 16;14:964077. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.964077. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36185487 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium- and/or Zinc-Enriched Egg Diet Improves Oxidative Damage and Regulates Gut Microbiota in D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 13;16(4):512. doi: 10.3390/nu16040512. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398836 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid protects motor function and increases dopamine synthesis in a rat model of Parkinson's disease via mechanisms associated with increased protein kinase activity in the striatum.Neuropharmacology. 2020 May 1;167:107976. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.107976. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32001239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayon Y, Croset M, Lagarde M, Lecerf J, Thies F, Tayot JL, Chirouze V (1997) Polyunsaturated fatty acid based drugs. US 5654290 A
-
- Blokland A, Honig W, Brouns F, Jolles J (1999) Cognition-enhancing properties of subchronic phosphatidylserine (PS) treatment in middle-aged rats: comparison of bovine cortex PS with egg PS and soybean PS. Nutrition 15:778–783 - PubMed
-
- Bonda DJ, Wang X, Perry G, Nunomura A, Tabaton M, Zhu X, Smith MA (2010) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: a possibility for prevention. Neuropharmacology 59:290–294. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.04.005 - PubMed
-
- Breckenridge WC, Gombos G, Morgan IG (1972) The lipid composition of adult rat brain synaptosomal plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 266:695–707 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

