Emulsified omega-3 fatty-acids modulate the symptoms of depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a pilot study
- PMID: 28690672
- PMCID: PMC5497377
- DOI: 10.1186/s13034-017-0167-2
Emulsified omega-3 fatty-acids modulate the symptoms of depressive disorder in children and adolescents: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of mood disorders in children is a growing global concern. Omega-3 fatty acids (FA) are emerging as a promising adjuvant therapy for depressive disorder (DD) in paediatric patients. The primary objective of this pilot, single-centre, randomized, double-blind controlled study was to compare the efficacy of an Omega-3 FA fish oil emulsion with a control oil emulsion alongside standard treatment for depressive symptoms in children and adolescents suffering from depressive disorder (DD) and mixed anxiety depressive disorder (MADD).
Methods: 38 children (12 patients were treated and diagnosed for at least 1 month before enrolment, 26 patients were first-time diagnosed as DD) aged 11-17 years were randomised 1:1 to the intervention (Omega-3 FA, 19 patients) or active comparator (Omega-6 FA, 19 patients) groups. Children's depression inventory (CDI) ratings were performed at baseline, every 2 weeks for a 12-week intervention period and at 4-week post-intervention. 35 patients (17 in Omega-3 and 18 in Omega-6 groups) who completed the whole intervention period were evaluated. Patients from Omega-3 group were stratified according to diagnosis into two subgroups (DD-10/17 and mixed anxiety depressive disorder (MADD)-7/17 patients) and in the Omega-6 group into DD-10/18 and MADD-8/18 patients. Groups were evaluated separately. Differences between-groups were tested with the Student´s t test or non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures and Friedman test were used to analyse the Treatment effect for response in CDI score. p < 0.05 was considered significant in all statistical analyses.
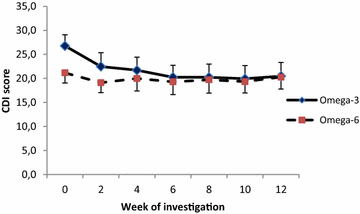
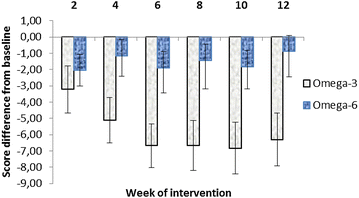
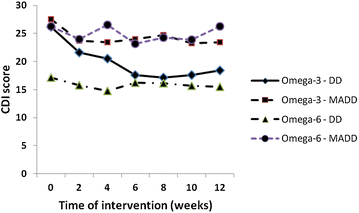
Results: Significant reductions in CDI scores in 35 analysed patients who completed 12 weeks intervention were observed after 12 weeks of intervention only in the Omega-3 group (p = 0.034). After stratification to depressive disorder and mixed anxiety depressive disorder subgroups, the DD subgroup receiving the Omega-3 FA fish oil showed statistically greater improvement (score reduction after 8 week treatment of -9.1 CDI, p = 0.0001) when compared to the MADD subgroup (score reduction after 8 week treatment -4.24 CDI, p = 0.271).
Conclusions: CDI scores were reduced in the Omega-3 group and the depression subgroup had greater improvement than the mixed depressive/anxiety group. An Omega-3 fatty acid rich fish oil emulsion may be an effective adjuvant supplement during the treatment of depressive disorders in children. Trial registration ISRCTN81655012.
Figures
References
-
- Costello J, Erkanli A, Angold A. Is there an epidemic of child or adolescent depression? J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2006;47:1263–1271. - PubMed
-
- Coghill D, Bonnar S, Duke S, Graham J, Seth S. Child and adolescent psychiatry. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2009. ISBN: 978-0-19-923499-8.
-
- Colin A, Reggers J, Castronovo V, Ansseau M. Lipds, depression and suicide. Encephale. 2003;29:49–58. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

