Sestrin2 as a Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Various Diseases
- PMID: 28690762
- PMCID: PMC5485329
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/3296294
Sestrin2 as a Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Various Diseases
Abstract
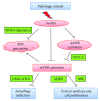
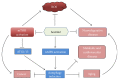
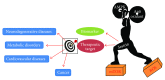
Sestrin2 (SESN2), a highly conserved stress-inducible metabolic protein, is known to repress reactive oxygen species (ROS) and provide cytoprotection against various noxious stimuli including genotoxic and oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and hypoxia. Studies demonstrate that the upregulation of Sestrin2 under conditions of oxidative stress augments autophagy-directed degradation of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), which targets and breaks down nuclear erythroid-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a key regulator of various antioxidant genes. Moreover, ER stress and hypoxia are shown to induce Sestrins, which ultimately reduce cellular ROS levels. Sestrin2 also plays a pivotal role in metabolic regulation through activation of the key energy sensor AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) and inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). Other downstream effects of Sestrins include autophagy activation, antiapoptotic effects in normal cells, and proapoptotic effects in cancer cells. As perturbations in the aforementioned pathways are well documented in multiple diseases, Sestrin2 might serve as a potential therapeutic target for various diseases. Thus, the aim of this review is to discuss the upstream regulators and the downstream effectors of Sestrins and to highlight the significance of Sestrin2 as a biomarker and a therapeutic target in diseases such as metabolic disorders, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Tsilioni I., Filippidis A. S., Kerenidi T., Budanov A. V., Zarogiannis S. G., Gourgoulianis K. I. Sestrin-2 is significantly increased in malignant pleural effusions due to lung cancer and is potentially secreted by pleural mesothelial cells. Clinical Biochemistry. 2016;49(9):726–728. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.02.002. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

