Imbalances in T Cell-Related Transcription Factors Among Patients with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- PMID: 28690889
- PMCID: PMC5488818
- DOI: 10.18295/squmj.2016.17.02.007
Imbalances in T Cell-Related Transcription Factors Among Patients with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Abstract
Objectives: Imbalances in effector T cell functioning have been associated with a number of autoimmune diseases, including Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT). Differentiation of effector T helper (Th) 1, Th2, Th17 and regulatory T cell (Treg) lymphocytes is regulated by transcription factors, including Th1-specific T box (T-bet), GATA binding protein-3 (GATA3), retinoid-related orphan receptor (ROR)-α and forkhead box P3 (FOXP3). This study aimed to investigate Th1/Th2, Th1/Treg, Th2/Treg and Th17/Treg balances at the level of these transcription factors.
Methods: This study took place between October 2015 and August 2016. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected from a control group of 40 healthy women recruited from the Zahedan University of Medical Sciences, Zahedan, Iran, and a patient group of 40 women with HT referred to the Hazrat Ali Asghar Hospital, Zahedan. Total ribonucleic acid extraction was performed and the gene expression of transcription factors was quantitated using a real-time polymerase chain reaction technique.
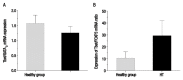
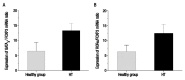
Results: Expression of T-bet and GATA3 was significantly elevated, while FOXP3 expression was significantly diminished among HT patients in comparison with the controls (P = 0.03, 0.01 and 0.05, respectively). Expression of RORα was higher among HT patients, although this difference was not significant (P = 0.15). Expression of T-bet/FOXP3, GATA3/FOXP3 and RORα/FOXP3 ratios were increased among HT patients in comparison with the controls (P <0.02, <0.01 and <0.01, respectively).
Conclusion: These results indicate that HT patients have imbalances in Th1/Treg, Th2/Treg and Th17/Treg lymphocytes at the level of the transcription factors, deviating towards Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells. Correction of these imbalances may therefore be therapeutic.
Keywords: Hashimoto Thyroiditis; Lymphocytes; Regulatory T Cells; Th1 Cells; Th17 Cells; Th2 Cells; Transcription Factors.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cogni G, Chiovato L. An overview of the pathogenesis of thyroid autoimmunity. Hormones (Athens) 2013;12:19–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
