The state of gene therapy research in Africa, its significance and implications for the future
- PMID: 28692018
- PMCID: PMC7094717
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2017.57
The state of gene therapy research in Africa, its significance and implications for the future
Abstract
Gene therapy has made impressive recent progress and has potential for treating a wide range of diseases, many of which are important to Africa. However, as a result of lack of direct public funding and skilled personnel, direct research on gene therapy in Africa is currently limited and resources to support the endeavor are modest. A strength of the technology is that it is based on principles of rational design, and the tools of gene therapy are now highly versatile. For example gene silencing and gene editing may be used to disable viral genes for therapeutic purposes. Gene therapy may thus lead to cure from infections with HIV-1, hepatitis B virus and Ebola virus, which are of significant public health importance in Africa. Although enthusiasm for gene therapy is justified, significant challenges to implementing the technology remain. These include ensuring efficient delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids to target cells, limiting unintended effects, cost and complexity of treatment regimens. In addition, implementation of effective legislation that will govern gene therapy research will be a challenge. Nevertheless, it is an exciting prospect that gene therapy should soon reach the mainstream of medical management. Participation of African researchers in the exciting developments is currently limited, but their involvement is important to address health problems, develop capacity and enhance economic progress of the continent.
Conflict of interest statement
PA, MBM and AE receive funding from Johnson & Johnson Innovation. MSP does not declare any conflict of interest.
Figures
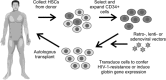
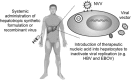
References
-
- Friedmann T, Roblin R. Gene therapy for human genetic disease? Science. 1972;175:949–955. - PubMed
-
- Naldini L. Gene therapy returns to centre stage. Nature. 2015;526:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Ely A, Naidoo T, Mufamadi S, Crowther C, Arbuthnot P. Expressed anti-HBV primary microRNA shuttles inhibit viral replication efficiently in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther. 2008;16:1105–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

