Emerging roles of the histone chaperone CAF-1 in cellular plasticity
- PMID: 28692904
- PMCID: PMC5813839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.06.004
Emerging roles of the histone chaperone CAF-1 in cellular plasticity
Abstract
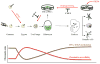
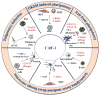
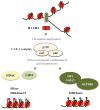
During embryonic development, cells become progressively restricted in their differentiation potential. This is thought to be regulated by dynamic changes in chromatin structure and associated modifications, which act together to stabilize distinct specialized cell lineages. Remarkably, differentiated cells can be experimentally reprogrammed to a stem cell-like state or to alternative lineages. Thus, cellular reprogramming provides a valuable platform to study the mechanisms that normally safeguard cell identity and uncover factors whose manipulation facilitates cell fate transitions. Recent work has identified the chromatin assembly factor complex CAF-1 as a potent barrier to cellular reprogramming. In addition, CAF-1 has been implicated in the reversion of pluripotent cells to a totipotent-like state and in various lineage conversion paradigms, suggesting that modulation of CAF-1 levels may endow cells with a developmentally more plastic state. Here, we review these exciting results, discuss potential mechanisms and speculate on the possibility of exploiting chromatin assembly pathways to manipulate cell identity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- De Los Angeles A, Ferrari F, Xi R, Fujiwara Y, Benvenisty N, Deng H, Hochedlinger K, Jaenisch R, Lee S, Leitch HG, Lensch MW, Lujan E, Pei D, Rossant J, Wernig M, Park PJ, Daley GQ. Hallmarks of pluripotency. Nature. 2015;525:469–478. - PubMed
-
- Seisenberger S, Peat JR, Reik W. Conceptual links between DNA methylation reprogramming in the early embryo and primordial germ cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013;25:281–288. - PubMed
-
- Ishiuchi T, Torres-Padilla ME. Towards an understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of totipotency. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013;23:512–518. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Huang B, Chen H, Yin Q, Liu Y, Xiang Y, Zhang B, Liu B, Wang Q, Xia W, Li W, Li Y, Ma J, Peng X, Zheng H, Ming J, Zhang W, Zhang J, Tian G, Xu F, Chang Z, Na J, Yang X, Xie W. The landscape of accessible chromatin in mammalian preimplantation embryos. Nature. 2016;534:652–657. Using an improved version of ATAC-seq technology, the authors provide evidence for a unique chromatin state at repetitive elements and transcriptional end sites during the first three cleavage divisions. They further identify broad ATAC-seq domains over MERVL retro-elements and non-repeat early 2-cell associated genes. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

