Prognostic significance of ABCB1 in stage I lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 28693170
- PMCID: PMC5494850
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6145
Prognostic significance of ABCB1 in stage I lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
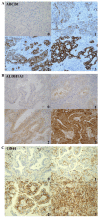
Cancer stem cell (CSC) properties have been recently proposed to explain tumor carcinogenesis and multidrug resistance in several human cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The present study examined the protein expression of three CSC-associated markers, namely ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 (ABCB1), aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1 (ALDH1A1) and cluster of differentiation (CD) 44, by immunohistochemistry in 194 NSCLC patients who underwent complete resection of NSCLC tumors. The association between the expression of these proteins and patient prognosis was evaluated to clarify the prognostic significance of CSC-associated markers in NSCLC patients. Positive staining for ABCB1 demonstrated a trend toward worse survival compared with negative staining in stage I-III NSCLC. Negative staining for ALDH1 or CD44 exhibited a trend toward worse survival compared with positive staining in stage I-III NSCLC. It was observed that patients with stage I lung adenocarcinoma (ADC) showing positivity for ABCB1 expression had significantly poorer survival than those with negative ABCB1 staining (P=0.03). Furthermore, stage I ADC patients with wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) who exhibited positive staining for ABCB1 had significantly shorter disease-free survival (DFS) compared with patients with negative staining for ABCB1 (P<0.01). Analyses by univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards models revealed that ABCB1-positive staining was significantly associated with DFS and was an independent prognostic factor (hazard ratio, 3.49; P<0.05) in these patients. These results suggest that ABCB1 protein expression is useful for predicting prognosis and selecting patients for post-operative therapy in stage I lung ADC patients, particularly those harboring wild-type EGFR.
Keywords: ABCB1; EGFR; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combination of PD-L1 expression and NLR as prognostic marker in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 22;10(26):6703-6710. doi: 10.7150/jca.34469. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31777599 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of cancer stem cell-related markers in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with induction chemoradiotherapy.Lung Cancer. 2012 Jul;77(1):162-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 3. Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22387005
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1/epidermal growth factor receptor coexpression is characteristic of a highly aggressive, poor-prognosis subgroup of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 2013 Aug;44(8):1465-71. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2012.12.016. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Hum Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23465277
-
NQO1 protein expression predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancers.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 31;15:207. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1227-8. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25880877 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of EGFR mutations in surgically resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct;13(5):e204-e211. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12512. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27349355
Cited by
-
Upregulation of Chemoresistance by Mg2+ Deficiency through Elevation of ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily B Member 1 Expression in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells.Cells. 2021 May 12;10(5):1179. doi: 10.3390/cells10051179. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34066059 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of the Drug Tezosentan for Cancer Therapy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jun 11;45(6):5118-5131. doi: 10.3390/cimb45060325. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37367074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Influencing Mortality in Children with Central Nervous System Tumors: A Cohort Study on Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Markers.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;15(4):473. doi: 10.3390/genes15040473. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674407 Free PMC article.
-
ABCB1 and ABCC1 Function during TGF-β-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: Relationship between Multidrug Resistance and Tumor Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 23;24(7):6046. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076046. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047018 Free PMC article.
-
CADM1 and SPC25 Gene Mutations in Lung Cancer Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021 Sep 24;2(11):100232. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100232. eCollection 2021 Nov. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2021. PMID: 34746885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–128. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
