Efficacy and safety of SOX chemotherapy with or without surgery in AFP-producing advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 28693208
- PMCID: PMC5494698
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.6240
Efficacy and safety of SOX chemotherapy with or without surgery in AFP-producing advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
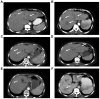
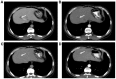
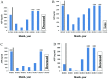
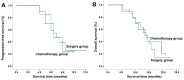
The present study investigated the clinical efficacy of S-1 plus oxaliplatin (SOX) regimen, with or without surgery in α-fetoprotein-producing gastric cancer (APGC) with liver metastasis. A total of 24 patients with APGC treated at the Liaocheng People's Hospital between January 2011 and December 2013 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical efficacy and patient safety were compared between the two groups. The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the SOX group were 6.5 [95% confidence interval (CI), 4.6-8.4] and 13.5 (95% CI, 8.1-18.9) months, respectively. The corresponding indicators in the SOX and surgery group were 7.0 (95% CI, 5.7-8.3) and 14 (95% CI, 11.0-17.1) months, respectively. There was no significant difference in PFS and OS between the two groups (P=0.703 and 0.710, respectively). The adverse effects of leucopenia, neutropenia, anemia and diarrhea occurred in ~10% of patients in the SOX group and in 14.3% (2/14), 7.14% (1/14), 14.3% (2/14) and 7.14% (1/14), respectively, in the surgery group. No significant difference was identified between groups in terms of overall incidence of adverse effects (P=0.17). However, severe adverse events, including gastroplegia, pancreatic fistula, pulmonary infection and refractory ascites, occurred only in the SOX plus surgery group [incidence rate for severe adverse events, 7.14% (1/14); P<0.001 between groups]. In conclusion, SOX chemotherapy is safe and effective in patients with APGC and liver metastasis. However, the addition of surgery to SOX chemotherapy may not improve the disease control rate and may increase the adverse effects.
Keywords: S-1 plus oxaliplatin regimen; liver metastasis; surgery; α-fetoprotein-producing gastric cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved efficacy and safety of low-dose oxaliplatin/pegylated liposomal doxorubicin/S-1 regimen in advanced gastric cancer: a cohort study.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):12821-12830. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3584. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 35016420
-
Comparison of S-1 plus oxaliplatin (SOX) and capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (XELOX) as adjuvant chemotherapies for stage II and III gastric cancer after D2 resection: A single-center retrospective study.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;16(3):180-186. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13321. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32077628 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1 plus oxaliplatin improves survival of patients with gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy: A multicenter propensity score-matched study.World J Clin Cases. 2018 Sep 26;6(10):373-383. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i10.373. World J Clin Cases. 2018. PMID: 30283800 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis supporting noninferiority of oxaliplatin plus S-1 to cisplatin plus S-1 in first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (G-SOX study): indirect comparison with S-1 alone.Int J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug;21(4):668-675. doi: 10.1007/s10147-015-0938-9. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26733020 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Xiao Ai Ping Injection Combined with Chemotherapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 May 19;2019:3821053. doi: 10.1155/2019/3821053. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31236124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Clinicopathological Characteristics of Alpha-Fetoprotein-Producing Adenocarcinoma of the Gastrointestinal Tract-A Single-Center Retrospective Study.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 29;11:635537. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.635537. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996549 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine metabolism genes prognostic signature for stomach adenocarcinoma and immune infiltration: potential biomarkers for predicting overall survival.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 12;13:1201297. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1201297. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37377916 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of combination chemotherapy administration on prognostic outcomes in stage II and III gastric cancer: a comprehensive analysis utilizing propensity score matching.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Jan 15;17(1):377-395. doi: 10.62347/WVYP2688. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39959247 Free PMC article.
-
High serum alpha-fetoprotein and positive immunohistochemistry of alpha-fetoprotein are related to poor prognosis of gastric cancer with liver metastasis.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 14;14(1):3695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54394-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38355790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP)-producing gastric cancer: clinicopathological features and treatment strategies.Cell Biosci. 2025 Jun 10;15(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13578-025-01424-8. Cell Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40495217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ooi A, Nakanishi I, Sakamoto N, Tsukada Y, Takahashi Y, Minamoto T, Mai M. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)-producing gastric carcinoma. Is it hepatoid differentiation? Cancer. 1990;65:1741–1747. - PubMed
-
- Jia Y, Liu D, Xiao D, Ma X, Han S, Zheng Y, Sun S, Zhang M, Gao H, Cui X, Wang Y. Expression of AFP and STAT3 is involved in arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation in AFP-producing gastric cancer cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e54774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054774. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu DP, He QJ, Liu CG. Correlations among Helicobacter pylori infection and the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:795–799. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.06168.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
