Warm-needling acupuncture and medicinal cake-separated moxibustion for hyperlipidemia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28693531
- PMCID: PMC5504830
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2029-x
Warm-needling acupuncture and medicinal cake-separated moxibustion for hyperlipidemia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture and moxibustion has been widely applied to hyperlipidemia treatment in clinical practice in China, serving as an alternative treatment to statins. Warm-needling acupuncture and medicinal cake-separated moxibustion have been separately reported with potential therapeutic effects on hyperlipidemia treatment in several studies but with limitations in study methodology. Combining these two modalities may provide a more advantageous strategy in treating hyperlipidemia. Therefore, a strict evaluation through well-designed randomized controlled trials (RCT) is necessary to determine their efficacy and safety on hyperlipidemia.
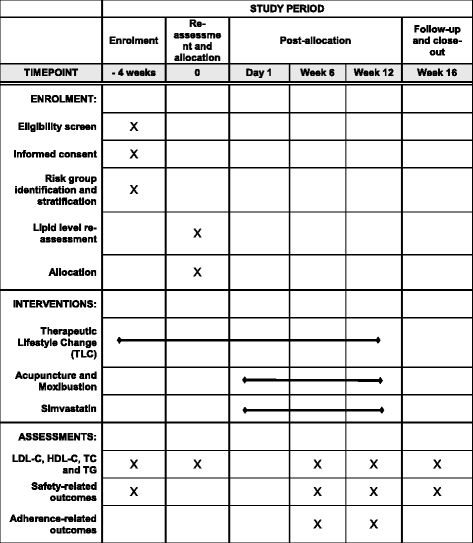
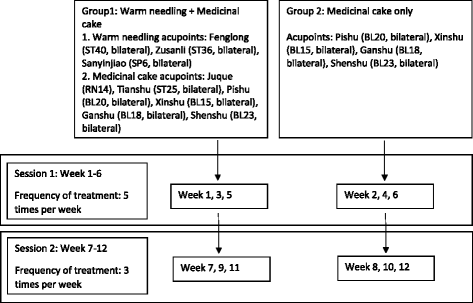
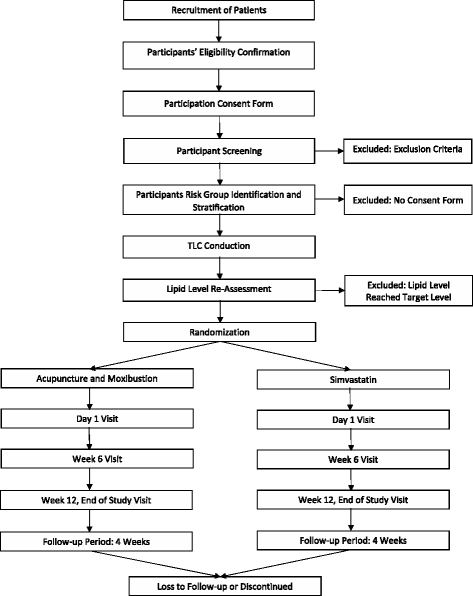
Methods: The study a multicenter, open-label, randomized, stratified, active-controlled, noninferiority trial with two parallel groups. Subjects with hyperlipidemia will be stratified into different groups by risk levels of heart diseases. They then will be instructed to the Therapeutic Lifestyle Change (TLC) diet. Those who have not reached the target lipid level will be randomly assigned to the treatments of either acupuncture and moxibustion or simvastatin with a 1:1 allocation. One hundred and thirty subjects are aimed to be recruited. The duration of intervention for this study will be 12 weeks, followed by another 4 weeks for post-treatment assessment. The primary outcome is percentage change from baseline to the end of the study in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Other indicators in lipid change, safety and adherence will also be assessed secondarily. The repeated measures, linear mixed-effects model will be applied to the analysis.
Discussion: Acupuncture and moxibustion could be a potentially effective treatment alternative for hyperlipidemia. A study with careful design is developed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combined acupuncture and moxibustion, by integrating the traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) regimens with the standardized Western medicine appraisal approach.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02269046 . Registered on 26 September 2014.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Hyperlipidemia; Medicinal cake-separated moxibustion; Moxibustion; Randomized controlled trial; Traditional Chinese medicine; Warm-needling acupuncture.
Figures
References
-
- Feingold K. Statin therapy in hyperlipidemia: balancing the risk and benefits. 2014.
-
- 张宝珍, 张凯, 刘玉珍. 针灸丰隆治疗高脂血症临床随机对照试验 Meta 分析. 中国中医药信息杂志 2014;21:11-15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

