Post-exposure treatment with the oxime RS194B rapidly reverses early and advanced symptoms in macaques exposed to sarin vapor
- PMID: 28693885
- PMCID: PMC5586507
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.07.003
Post-exposure treatment with the oxime RS194B rapidly reverses early and advanced symptoms in macaques exposed to sarin vapor
Abstract
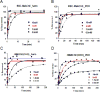
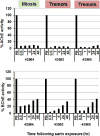
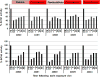
Organophosphate (OP) nerve agents and pesticides trigger a common mechanism of neurotoxicity resulting from critical targeting and inhibition of acetylcholinesterases (AChE) in central and peripheral synapses in the cholinergic nervous system. Therapeutic countermeasures have thus focused on either administering an oxime post-exposure, that can rapidly reactivate OP-inhibited AChE, or by preventing OP poisoning through administering pre-exposure treatments that scavenge OPs before they inhibit their physiological AChE targets. While several pyridinium aldoxime antidotes are currently approved, their utility is impaired due to their inability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) efficiently. The present study utilized a macaque (Ma) model to demonstrate the efficacy of a novel zwitterionic and centrally acting oxime RS194B to reactivate sarin- and paraoxon-inhibited macaque AChE and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) in vitro and to further assess the capacity of RS194B to effect a reversal of clinical symptoms following sarin inhalation in vivo. In vitro, oxime reactivation of MaAChE and MaBChE was shown to be comparable to their human orthologs, while the macaque studies indicated that IM administration of 62.5 mg/kg of RS194B and 0.28 mg/kg atropine after continuous exposure to 49.6 μg/kg sarin vapor, rapidly reactivated the inhibited AChE and BChE in blood and reversed both early and advanced clinical symptoms of sarin-induced toxicity following pulmonary exposure within 1 h. The rapid cessation of autonomic and central symptoms, including convulsions, observed in macaques bodes well for the use of RS194B as an intra- or post-exposure human treatment and validates the macaque model in generating efficacy and toxicology data required for approval under the FDA Animal rule.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
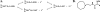
References
-
- Taylor P. Anticholinesterases. In: Brunton LL, editor. Goodman and Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 12. Chapter 10. 2009. pp. 239–254. 13th Edition, July 2017.
-
- Somani SM, Romano JA., Jr . Chemical Warfare Agents: Toxicity at Low Levels. CRC Press; Boca Raton: 2001. p. 447.
-
- Gupta RC. Toxicology of Organophosphate & Carbamate Compounds. Academic Press; New York: 2006. p. 763.
-
- Shih T-M, Koplovitz I, Kan RK, McDonough JH. In search of an effective in vivo reactivator for organophosphorus nerve agent-inhibited acetylcholinesterase in the central nervous system. Advanced Studies in Biology. 2012;4:451–478.
-
- Wilson IB, Ginsburg S. Reactivation of acetylcholinesterase inhibited by alkylphosphates. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1955;54:569–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

