Emerging role for dysregulated decidualization in the genesis of preeclampsia
- PMID: 28693893
- PMCID: PMC5718949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2017.06.005
Emerging role for dysregulated decidualization in the genesis of preeclampsia
Abstract
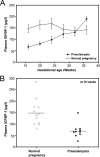
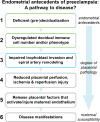
In normal human placentation, uterine invasion by trophoblast cells and subsequent spiral artery remodeling depend on cooperation among fetal trophoblasts and maternal decidual, myometrial, immune and vascular cells in the uterine wall. Therefore, aberrant function of anyone or several of these cell-types could theoretically impair placentation leading to the development of preeclampsia. Because trophoblast invasion and spiral artery remodeling occur during the first half of pregnancy, the molecular pathology of fetal placental and maternal decidual tissues following delivery may not be informative about the genesis of impaired placentation, which transpired months earlier. Therefore, in this review, we focus on the emerging prospective evidence supporting the concept that deficient or defective endometrial maturation in the late secretory phase and during early pregnancy, i.e., pre-decidualization and decidualization, respectively, may contribute to the genesis of preeclampsia. The first prospectively-acquired data directly supporting this concept were unexpectedly revealed in transcriptomic analyses of chorionic villous samples (CVS) obtained during the first trimester of women who developed preeclampsia 5 months later. Additional supportive evidence arose from investigations of Natural Killer cells in first trimester decidua from elective terminations of women with high resistance uterine artery indices, a surrogate for deficient trophoblast invasion. Last, circulating insulin growth factor binding protein-1, which is secreted by decidual stromal cells was decreased during early pregnancy in women who developed preeclampsia. We conclude this review by making recommendations for further prospectively-designed studies to corroborate the concept of endometrial antecedents of preeclampsia. These studies could also enable identification of women at increased risk for developing preeclampsia, unveil the molecular mechanisms of deficient or defective (pre)decidualization, and lead to preventative strategies designed to improve (pre)decidualization, thereby reducing risk for preeclampsia development.
Keywords: Decidua; Endometrium; Immune cells; Maternal-fetal interface; Placenta; Trophoblast.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ilekis JV, Tsilou E, Fisher S, Abrahams VM, Soares MJ, Cross JC, Zamudio S, Illsley NP, Myatt L, Colvis C, Costantine MM, Haas DM, Sadovsky Y, Weiner C, Rytting E, Bidwell G. Placental origins of adverse pregnancy outcomes: potential molecular targets: an Executive Workshop Summary of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health Human Development. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(1 Suppl):S1–S46. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pijnenborg R, Vercruysse L, Hanssens M, Brosens I. Endovascular trophoblast and preeclampsia: A reassessment. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2011;1(1):66–71. - PubMed
-
- Brosens IA, Robertson WB, Dixon HG. The role of the spiral arteries in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol Annu. 1972;1:177–91. - PubMed
-
- Lyall F, Robson SC, Bulmer JN. Spiral artery remodeling and trophoblast invasion in preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction: relationship to clinical outcome. Hypertension. 2013;62(6):1046–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

