Peritransplant Soluble CD30 as a Risk Factor for Slow Kidney Allograft Function, Early Acute Rejection, Worse Long-Term Allograft Function, and Patients' Survival
- PMID: 28694560
- PMCID: PMC5485490
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9264904
Peritransplant Soluble CD30 as a Risk Factor for Slow Kidney Allograft Function, Early Acute Rejection, Worse Long-Term Allograft Function, and Patients' Survival
Abstract
Background: We aimed to determine whether serum soluble CD30 (sCD30) could identify recipients at high risk for unfavorable early and late kidney transplant outcomes.
Methods: Serum sCD30 was measured on the day of kidney transplantation and on the 4th day posttransplant. We assessed the value of these measurements in predicting delayed graft function, slow graft function (SGF), acute rejection (AR), pyelonephritis, decline of allograft function after 6 months, and graft and patient survival during 5 years of follow-up in 45 recipients.
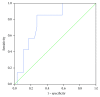
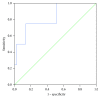
Results: We found the association between low pretransplant serum levels of sCD30 and SGF. The absence of significant decrease of sCD30 on the 4th day posttransplant was characteristic for SGF, early AR (the 8th day-6 months), late AR (>6 months), and early pyelonephritis (the 8th day-2 months). Lower pretransplant and posttransplant sCD30 predicted worse allograft function at 6 months and 2 years, respectively. Higher pretransplant sCD30 was associated with higher frequency of early AR, and worse patients' survival, but only in the recipients of deceased-donor graft. Pretransplant sCD30 also allowed to differentiate patients with early pyelonephritis and early AR.
Conclusions: Peritransplant sCD30 is useful in identifying patients at risk for unfavorable early and late transplant outcomes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Soluble CD30, the Immune Response, and Acute Rejection in Human Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 28;11:295. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00295. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32256486 Free PMC article.
-
Posttransplant soluble CD30 as a predictor of acute renal allograft rejection.Exp Clin Transplant. 2009 Dec;7(4):237-40. Exp Clin Transplant. 2009. PMID: 20353374
-
Pre-transplant and post-transplant soluble CD30 for prediction and diagnosis of acute kidney allograft rejection.Int Urol Nephrol. 2009;41(3):687-93. doi: 10.1007/s11255-008-9505-x. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Int Urol Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19142743
-
Identification of highly responsive kidney transplant recipients using pretransplant soluble CD30.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002 Jun;13(6):1650-6. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000014256.75920.5b. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002. PMID: 12039995
-
Pretransplantation soluble CD30 level as a predictor of acute rejection in kidney transplantation: a meta-analysis.Transplantation. 2012 Nov 15;94(9):911-8. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31826784ad. Transplantation. 2012. PMID: 23052636 Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble CD30, the Immune Response, and Acute Rejection in Human Kidney Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 28;11:295. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00295. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32256486 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on Biomarkers of Early and Late Kidney Graft Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5404. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155404. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

