Helicobacter pylori BabA in adaptation for gastric colonization
- PMID: 28694656
- PMCID: PMC5483490
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i23.4158
Helicobacter pylori BabA in adaptation for gastric colonization
Abstract
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) as a causative agent of gastric complications, is well adapted for the colonization of gastric mucosa. Although the infectious process depends on several factors, the adhesion to the gastric mucosa is the first and important step. Among several outer membrane proteins, BabA is one of the significant protein involving in many inflammatory processes in addition to its role in the attachment for the persistent colonization. We performed a PubMed search using the key words: "babA", "pylori", "gastric complications", "homologous recombination", "slipped strand mispairing"; a total of 249 articles were displayed. Of these we mainly focused on articles with the full text in English and published between 2005 and 2016. H. pylori BabA is involved in binding with receptors; however, its synthesis is regulated by phase variation. In this review we confirm that H. pylori babA can be modulated at the molecular and functional levels to adapt to the stress within the gastro-intestinal tract.
Keywords: BabA; Gastric complications; Helicobacter pylori; Homologous recombination; Slipped strand mispairing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no any conflict of interests.
Figures

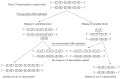
References
-
- IARC Helicobacter pylori Working Group. Helicobacter pylori Eradication as a Strategy for Preventing Gastric Cancer. Lyon, France 2014: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC Working Group Reports, No. 8) Available from: http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfsonline/wrk/wrk8/index.php.
-
- Plummer M, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Forman D, de Martel C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:487–490. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

