Electro-pharmacological profiles of two brain mitoplast anion channels: Inferences from single channel recording
- PMID: 28694756
- PMCID: PMC5491910
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2016-808
Electro-pharmacological profiles of two brain mitoplast anion channels: Inferences from single channel recording
Abstract
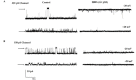
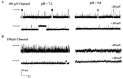
We have characterized the conduction and blocking properties of two different chloride channels from brain mitochondrial inner membranes after incorporation into planar lipid bilayers. Our experiments revealed the existence of channels with a mean conductance of 158 ± 7 and 301 ± 8 pS in asymmetrical 200 mM cis/50 mM trans KCl solutions. We determined that the channels were ten times more permeable for Cl- than for K+, calculated from the reversal potential using the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation. The channels were bell-shaped voltage dependent, with maximum open probability 0.9 at ± 20 mV. Two mitochondrial chloride channels were blocked after the addition of 10 µM DIDS. In addition, 158 pS chloride channel was blocked by 300 nM NPPB, acidic pH and 2.5 mM ATP, whereas the 301 pS chloride channel was blocked by 600 µM NPPB but not by acidic pH or ATP. Gating and conducting behaviors of these channels were unaffected by Ca2+. These results demonstrate that the 158 pS anion channel present in brain mitochondrial inner membrane, is probably identical to IMAC and 301 pS Cl channel displays different properties than those classically described for mitochondrial anion channels.
Keywords: brain; chloride channels; intracellular ion channels; mitochondria; mitoplast; single channel.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of a chloride-selective channel from rough endoplasmic reticulum membranes of rat hepatocytes: evidence for a block by phosphate.J Membr Biol. 1997 Oct 1;159(3):219-29. doi: 10.1007/s002329900285. J Membr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9312211
-
Stilbene derivatives inhibit the activity of the inner mitochondrial membrane chloride channels.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2007;12(4):493-508. doi: 10.2478/s11658-007-0019-9. Epub 2007 Apr 25. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17457523 Free PMC article.
-
A component of platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) venom forms slow-kinetic cation channels.J Membr Biol. 1999 Nov 1;172(1):37-45. doi: 10.1007/s002329900581. J Membr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10552012 Review.
-
Two types of chloride channel in the basolateral membrane of vestibular dark cells.Hear Res. 1993 Sep;69(1-2):124-32. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(93)90100-f. Hear Res. 1993. PMID: 8226332
-
Modulation of inner mitochondrial membrane channel activity.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Feb;24(1):99-110. doi: 10.1007/BF00769536. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992. PMID: 1380510 Review.
Cited by
-
40 Hz light preserves synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial function in Alzheimer's disease model.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 6;14(1):26949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78528-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39506052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aon MA, Cortassa S, Marban E, O'Rourke B. Synchronized whole cell oscillations in mitochondrial metabolism triggered by a local release of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:44735–44744. - PubMed
-
- Arsenijevic D, Onuma H, Pecqueur C, Raimbault S, Manning BS, Miroux B, et al. Disruption of the uncoupling protein-2 gene in mice reveals a role in immunity and reactive oxygen species production. Nat Genet. 2000;26:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Ashley RH. Challenging accepted ion channel biology: p64 and the CLIC family of putative intracellular anion channel proteins. Mol Membr Biol. 2003;20:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Avery J, Jahn R, Edwardson JM. Reconstitution of regulated exocytosis in cell-free systems: a critical appraisal. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:777–807. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
