The effects of prolonged CO2 insufflation on kidney function in a rat pneumoperitoneum model
- PMID: 28694897
- PMCID: PMC5502337
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2017.67210
The effects of prolonged CO2 insufflation on kidney function in a rat pneumoperitoneum model
Abstract
Introduction: Pneumoperitoneum (PP) is known to cause ischemia in kidneys and other intra-abdominal organs because of decreased splanchnic blood flow.
Aim: We aimed to determine the degree of renal injury that occurs due to a PP and prolonged PP. We measured renal injury biomarkers and made a histopathological evaluation to estimate the degree of injury and assessed the correlation of biomarkers with histopathological findings.
Material and methods: Twenty-one female Sprague Dawley rats were separated randomly into three groups. Group 1 was the control group and was given anesthesia for 3 h. In group 2, a PP was administered under anesthesia for 1 h. A pneumoperitoneum was administered under anesthesia to animals in group 3 for 3 h.
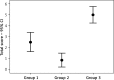
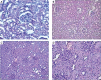
Results: Pathological analysis showed a significant statistical difference between the 3 groups. In particular, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and cystatin C (Cys C) levels at the 24th h and preoperative mean urea levels showed a significant difference between the groups. The 24th-hour NGAL level in group 3 was significantly higher than that of group 1. The preoperative Cys C level was higher in group 1 than in either group 2 or 3. Cys C was decreased significantly in group 1 and increased significantly in both groups 2 and 3.
Conclusions: The increase in NGAL and Cys C levels directly correlated with the duration of PP and intra-abdominal pressure, and they are therefore good biomarkers in diagnosing acute renal injury in the early phase. Serum creatinine level is not a good biomarker in the early phase of renal injury.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; cystatin C; neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; pneumoperitoneum; rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kirsch AJ, Hensle TW, Chang DT, et al. Renal effects of CO2 insufflation: oliguria and acute renal dysfunction in a rat pneumoperitoneum model. Urology. 1994;43:453–9. - PubMed
-
- Dunn MD, McDougall EM. Renal physiology: laparoscopic considerations. Urol Clin North Am. 2000;27:609–14. - PubMed
-
- Paparella A, Noviello C, Romano M, et al. Local and systemic impact of pneumoperitoneum on prepuberal rats. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:453–7. - PubMed
-
- Chiu AW, Chang LS, Birkett DH, Babayan RK. The impact of pneumoperitoneum, pneumoretroperitoneum, and gasless laparoscopy on the systemic and renal hemodynamic. J Am Coll Surg. 1995;181:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Price HL. Effects of carbon dioxide on the cardiovascular system. Anesthesiology. 1960;21:652–63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
