Tuberculosis treatment success among rural and urban Ugandans living with HIV: a retrospective study
- PMID: 28695082
- PMCID: PMC5493090
- DOI: 10.5588/pha.16.0115
Tuberculosis treatment success among rural and urban Ugandans living with HIV: a retrospective study
Abstract
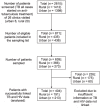
Setting: Government health centres and hospitals (six urban and 20 rural) providing tuberculosis (TB) treatment for people living with the human immunodeficiency virus (PLHIV) in central and western Uganda. Objective: To identify and quantify modifiable factors that limit TB treatment success among PLHIV in rural Uganda. Design: A retrospective cross-sectional review of routine Uganda National Tuberculosis and Leprosy Programme clinic registers and patient files of HIV-positive patients who received anti-tuberculosis treatment in 2014. Results: Of 191 rural patients, 66.7% achieved treatment success compared to 81.1% of 213 urban patients. Adjusted analysis revealed higher average treatment success in urban patients than in rural patients (OR 3.95, 95%CI 2.70-5.78, P < 0.01, generalised estimating equation model). Loss to follow-up was higher and follow-up sputum smear results were less frequently recorded in TB clinic registers among rural patients. Patients receiving treatment at higher-level facilities in rural settings had greater odds of treatment success, while patients receiving treatment at facilities where drug stock-outs had occurred had lower odds of treatment success. Conclusion: Lower reported treatment success in rural settings is mainly attributed to clinic-centred factors such as treatment monitoring procedures. We recommend strengthening treatment monitoring and delivery.
Contexte: L'étude a été réalisée dans des centres de santé et des hôpitaux publics, six urbains et 20 ruraux, fournissant un traitement de la tuberculose (TB) aux personnes vivant avec le VIH (PVVIH) dans le centre et l'ouest de l'Ouganda.Objectif: Identifier et quantifier les facteurs modifiables qui limitent le succès du traitement de la TB parmi les PVVIH dans l'Ouganda rural.Schéma: Une revue rétrospective transversale des registres cliniques et des dossiers de patients du Programme national tuberculose et lèpre d'Ouganda pour les patients VIH positifs qui ont reçu un traitement de TB en 2014.Résultats: Parmi 191 patients ruraux, 66,7% ont eu un bon résultat de leur traitement, tandis que parmi 213 patients urbains, 81,1% ont eu un bon résultat. Une analyse ajustée a révélé un succès thérapeutique moyen plus élevé chez les patients urbains comparés aux patients ruraux (OR 3,95 ; IC95% 2,70–5,78 ; P < 0,01 ; modèle d'équation d'estimation généralisée). Les pertes de vue ont été plus élevées et les résultats de frottis de crachats de suivi ont été moins souvent enregistrés dans les registres des centres TB pour les patients ruraux. Les patients recevant un traitement dans des structures de plus haut niveau, toujours en zone rurale, avaient plus de chances d'avoir un succès thérapeutique. Les patients recevant leur traitement dans des structures où étaient survenues des ruptures de stock de médicaments avaient moins de chances de succès thérapeutique.Conclusion: Les taux plus faibles de succès du traitement rapportés en zone rurale sont en majorité attribués à des facteurs liés aux centres de santé, comme les procédures de suivi du traitement. Nous recommandons le renforcement de la fourniture et du suivi du traitement.
Marco de referencia: El estudio se llevó a cabo en centros de salud y hospitales del sector público, seis en entornos urbanos y 20 en medio rural y consistió en suministrar el tratamiento antituberculoso a las personas positivas frente al virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH) en la región central y occidental de Uganda.Objetivo: Determinar y cuantificar los factores modificables que limitan la eficacia del tratamiento antituberculoso en las personas positivas frente al VIH en las zonas rurales de Uganda.Método: Fue este un estudio transversal retrospectivo de análisis de los registros corrientes y las historias clínicas de los pacientes positivos frente al VIH, en los consultorios del Programa Nacional contra la Tuberculosis y la Lepra de Uganda en el 2014.Resultados: De los 191 pacientes de entornos rurales, el 66,7% logró un tratamiento eficaz y en los 213 pacientes en medio urbano esta proporción fue 81,1%. Un análisis ajustado reveló un promedio de éxito terapéutico más alto en los pacientes urbanos en comparación con los pacientes rurales (OR 3,95; IC95% de 2,70 a 5,78; P < 0,01, según un modelo de ecuaciones de estimación generalizadas). En medio rural, se observó una mayor pérdida durante el seguimiento y se consignaban con menor frecuencia los resultados de las baciloscopias de seguimiento en los registros de tuberculosis de los consultorios. Los pacientes que recibían tratamiento en los establecimientos de nivel de atención más alto en medio rural tenían mayores posibilidades de éxito terapéutico. Los pacientes que recibían tratamiento en centros que presentaban desabastecimientos de medicamentos tuvieron menos probabilidades de lograr un tratamiento eficaz.Conclusión: La menor proporción de éxito terapéutico notificada en los entornos rurales se debe en su mayor parte a factores que dependen del consultorio, como los procedimientos de supervisión del tratamiento. Se recomienda reforzar la supervisión y el suministro del tratamiento antituberculoso.
Keywords: PLHIV; TB; Uganda; hospital records; rural; urban.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: none declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. . Global tuberculosis report, 2016. WHO/HTM/TB/2016.13 Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2016.
-
- Republic of Uganda Ministry of Health. . The HIV and AIDS Uganda Country Progress Report 2014. Kampala, Uganda: Ministry of Health, 2015.
-
- Achen E. Improving tuberculosis treatment completion rates: experience from Gulu Regional Referral Hospital, Uganda. Chevy Chase, MD, USA: University Research Co, 2012.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
